Carrier trapping and confinement in Ge nanocrystals surrounded by Ge3N4
Scientific Reports Nature Publishing Group (2016)
Abstract:
We investigated the optical properties of Ge nanocrystals surrounded by Ge3N4. The broad emission ranging from infrared to blue is due to the dependence on the crystal size and preparation methods. Here, we report high resolution Photoluminescence (PL) attributed to emission from individual Ge nanocrystals (nc-Ge) spatially resolved using micro-photoluminescence and detailed using temperature and power-dependent photoluminescence studies. The measured peaks are shown to behave with excitonic characteristics and we argue that the spread of the nc-Ge peaks in the PL spectrum is due to different confinement energies arising from the variation in size of the nanocrystals.Carrier trapping and confinement in Ge nanocrystals surrounded by Ge3N4.
Scientific reports 6 (2016) 25449-25449
Abstract:
We investigated the optical properties of Ge nanocrystals surrounded by Ge3N4. The broad emission ranging from infrared to blue is due to the dependence on the crystal size and preparation methods. Here, we report high resolution Photoluminescence (PL) attributed to emission from individual Ge nanocrystals (nc-Ge) spatially resolved using micro-photoluminescence and detailed using temperature and power-dependent photoluminescence studies. The measured peaks are shown to behave with excitonic characteristics and we argue that the spread of the nc-Ge peaks in the PL spectrum is due to different confinement energies arising from the variation in size of the nanocrystals.Sensors: Plasmonic Gas Sensing Using Nanocube Patch Antennas (Advanced Optical Materials 4/2016)
Advanced Optical Materials Wiley 4:4 (2016) 644-644
Color depth modulation and resolution in Phase-Change Material nano-displays
Advanced Materials Wiley 28:23 (2016) 4720-4726
Abstract:
Color modulation has been a topic of longstanding interest in science and engineering given its multiple applications in display technology, smart glass, security marks and active optical components.[1,2] Passive elements such as optical coatings employing a wide range of materials, multilayer configurations or structured films have been extensively used in optical systems to obtain a full range of colors and spectral windows in both reflective and transmissive devices.[1–6] Moreover, active materials with unique physical or chemical properties such as electrochromism,[7–9] piezochromism,[10] plasmonic effect,[11] photoluminescence[12,13] and volatile phase-change materials[14] have been exploited for color modulation purposes. The dynamic modulation of optical properties by such materials has given rise to remarkable resolution, low dimensionality and low energy operation of displays.[15] However, a combination of both, i.e. a device with high resolution featuring offline color retention while still allowing full-gamut modulation, had been elusive or had required external chemical agents[16] until recently, when an optoelectronic framework using nonvolatile nucleation dominated phase-change materials (PCMs) was proposed to fill this gap by employing Ge2Sb2Te5 (GST) as the active bistable component.[17]Gain spectroscopy of solution-based semiconductor nanocrystals in tunable optical microcavities
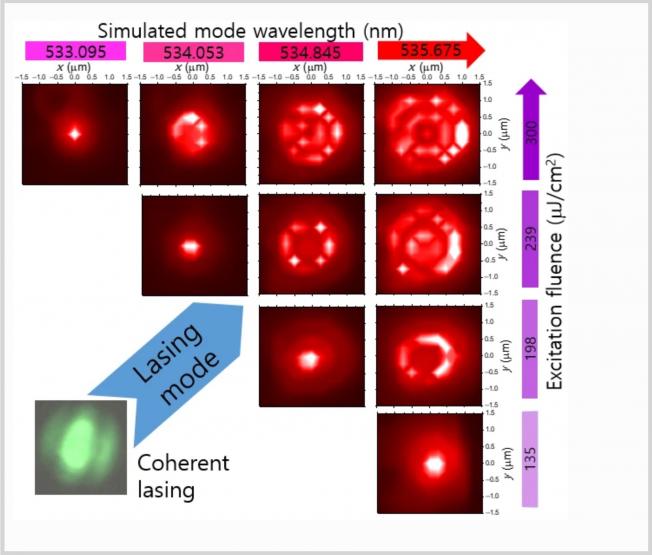
Advanced Optical Materials Wiley 4:2 (2016) 285-290