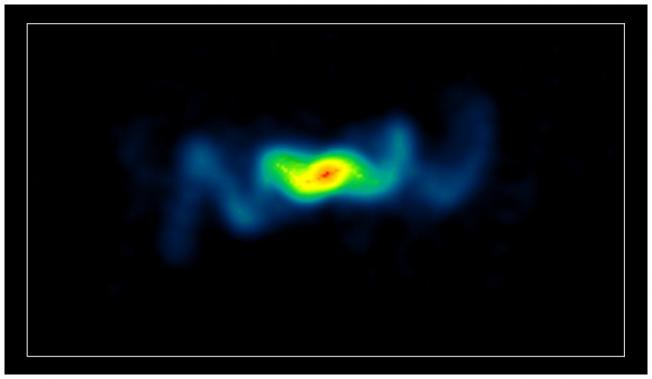
Jet propulsion of wind ejecta from a major flare in the black hole microquasar SS433
(2011)
SS433's accretion disc, wind and jets: before, during and after a major flare
ArXiv 1104.2917 (2011)
Abstract:
The Galactic microquasar SS433 occasionally exhibits a major flare when the intensity of its emission increases significantly and rapidly. We present an analysis of high-resolution, almost-nightly optical spectra obtained before, during and after a major flare, whose complex emission lines are deconstructed into single gaussians and demonstrate the different modes of mass loss in the SS433 system. During our monitoring, an initial period of quiescence was followed by increased activity which culminated in a radio flare. In the transition period the accretion disc of SS433 became visible in H-alpha and HeI emission lines and remained so until the observations were terminated; the line-of-sight velocity of the centre of the disc lines during this time behaved as though the binary orbit has significant eccentricity rather than being circular, consistent with three recent lines of evidence. After the accretion disc appeared its rotation speed increased steadily from 500 to 700 km/s. The launch speed of the jets first decreased then suddenly increased. At the same time as the jet launch speed increased, the wind from the accretion disc doubled in speed. Two days afterwards, the radio flux exhibited a flare. These data suggest that a massive ejection of material from the companion star loaded the accretion disc and the system responded with mass loss via different modes that together comprise the flare phenomena. We find that archival data reveal similar behaviour, in that when the measured jet launch speed exceeds 0.29c this is invariably simultaneous with, or a few days before, a radio flare. Thus we surmise that a major flare consists of the overloading of the accretion disc, resulting in the speeding up of the H-alpha rotation disc lines, followed by enhanced mass loss not just via its famous jets at higher-than-usual speeds but also directly from its accretion disc's wind.SS433's accretion disc, wind and jets: before, during and after a major flare
(2011)
Probing the history of SS433's jet kinematics via Decade-resolution radio observations of W50
ArXiv 1103.5658 (2011)
Abstract:
We present the results of a kinematical study of the W50 nebula using high resolution radio observations from the Very Large Array (VLA) spanning a 12-year period, sampled in 1984, 1993 and 1996. We conduct a careful analysis of the proper motions of the radio filaments across the W50 nebula at each epoch, and detect no significant motion for them during this period. The apparent lack of movement in the radio filaments mandates either (i) a high degree of deceleration of SS433's jet ejecta in the W50 nebula, or (ii) that the lobes of W50 formed a long time ago in SS433's history, during a jet outburst with appreciably different characteristics to the well-known precessing jet state observed in SS433 at the present day. We discuss the possible scenarios which could explain this result, with relevance to the nature of SS433's current jet activity.Probing the history of SS433's jet kinematics via Decade-resolution radio observations of W50
(2011)