The Subaru FMOS galaxy redshift survey (FastSound). V. Intrinsic alignments of emission-line galaxies at z ∼ 1.4
Publications of Astronomical Society of Japan Oxford University Press 70:3 (2018) 41
Abstract:
Intrinsic alignments (IA), the coherent alignment of intrinsic galaxy orientations, can be a source of a systematic error of weak lensing surveys. The redshift evolution of IA also contains information about the physics of galaxy formation and evolution. This paper presents the first measurement of IA at high redshift, z ∼ 1.4, using the spectroscopic catalog of blue star-forming galaxies of the FastSound redshift survey, with the galaxy shape information from the Canada–Hawaii–France telescope lensing survey. The IA signal is consistent with zero with power-law amplitudes fitted to the projected correlation functions for density–shape and shape–shape correlation components, Aδ+ = −0.0071 ± 0.1340 and A++ = −0.0505 ± 0.0848, respectively. These results are consistent with those obtained from blue galaxies at lower redshifts (e.g., Aδ+=0.0035+0.0387−0.0389 and A++=0.0045+0.0166−0.0168 at z = 0.51 from the WiggleZ survey). The upper limit of the constrained IA amplitude corresponds to a few percent contamination to the weak-lensing shear power spectrum, resulting in systematic uncertainties on the cosmological parameter estimations by −0.052 < Δσ8 < 0.039 and −0.039 < ΔΩm < 0.030.The hardware control system for WEAVE at the William Herschel telescope
GROUND-BASED AND AIRBORNE TELESCOPES VII SPIE 10700 (2018) ARTN 1070033
Abstract:
© 2018 SPIE. When an alt-azimuth telescope is tracking at a specific field, it is necessary to use a de-rotator system to compensate the Earth's rotation of the field of view. In order, to keep the telescope tracking the field of view selected, the instrument will need to a rotation system for compensating it [1]. The new WEAVE [2] two degrees field of view requires a new field de-rotator on the top-end of the telescope. The rotator system has been designed with a direct drive motor which eliminates the need for mechanical transmission elements such as gearboxes, speed reducers, and worm gear drives. This design is a huge advantage for the system performance and lifetime because it eliminates undesirable characteristics such as long-time drift, elasticity, and backlash. The hardware control system has been developed with a Rockwell servo-drive and controller. The rotator has to be controlled by the high-level software which is also responsible for the telescope control. This paper summarizes the model developed for simulating and the software which will be used to accept the rotator system. A performance study is also carried out to test the CIP (Common Industrial Protocol) for communications between the high-level software and the rotator hardware.VIRUS: status and performance of the massively-replicated fiber integral field spectrograph for the upgraded Hobby-Eberly Telescope
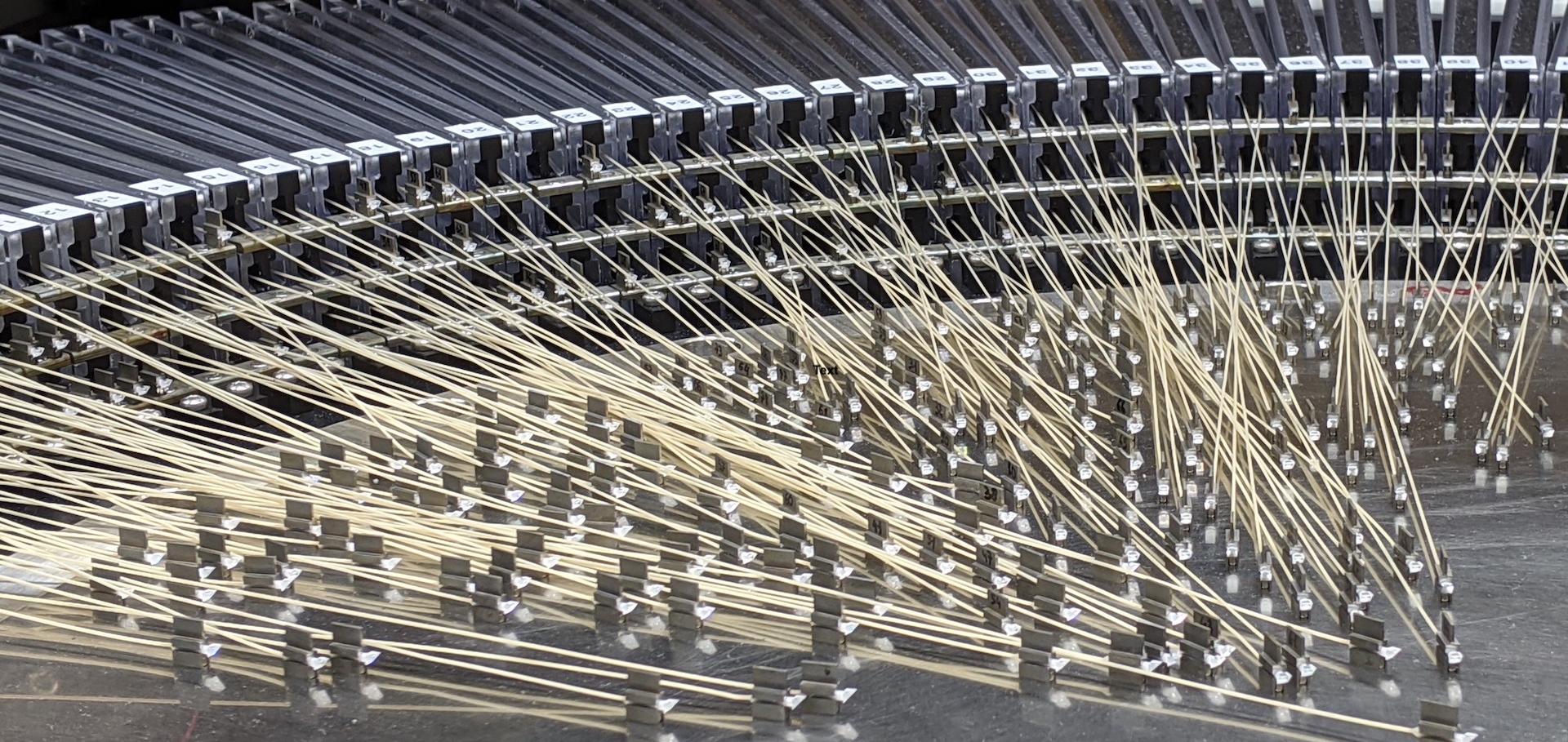
GROUND-BASED AND AIRBORNE INSTRUMENTATION FOR ASTRONOMY VII SPIE 10702 (2018) UNSP 107021K
Abstract:
© 2018 SPIE. The Visible Integral-field Replicable Unit Spectrograph (VIRUS) consists of 156 identical spectrographs (arrayed as 78 pairs, each with a pair of spectrographs) fed by 35,000 fibers, each 1.5 arcsec diameter, at the focus of the upgraded 10 m Hobby-Eberly Telescope (HET). VIRUS has a fixed bandpass of 350-550 nm and resolving power R∼750. The fibers are grouped into 78 integral field units, each with 448 fibers and 20 m average length. VIRUS is the first example of large-scale replication applied to optical astronomy and is capable of surveying large areas of sky, spectrally. The VIRUS concept offers significant savings of engineering effort and cost when compared to traditional instruments. The main motivator for VIRUS is to map the evolution of dark energy for the Hobby-Eberly Telescope Dark Energy Experiment (HETDEX), using 0.8M Lyman-alpha emitting galaxies as tracers. The VIRUS array has been undergoing staged deployment starting in late 2015. Currently, more than half of the array has been populated and the HETDEX survey started in 2017 December. It will provide a powerful new facility instrument for the HET, well suited to the survey niche of the telescope, and will open up large spectroscopic surveys of the emission line universe for the first time. We will review the current state of production, lessons learned in sustaining volume production, characterization, deployment, and commissioning of this massive instrument.The Subaru FMOS galaxy redshift survey (FastSound). V. Intrinsic alignments of emission line galaxies at $z\sim 1.4$
(2017)
Learning from history: adaptive calibration of 'tilting spine' fiber positioners
Astronomical Data Analysis Software and Systems XXV Astronomical Society of the Pacific (2017) 643-646