Single-shot measurement of temperature and pressure using laser-induced thermal gratings with a long probe pulse
APPLIED PHYSICS B-LASERS AND OPTICS 78:1 (2004) 111-117
Single-shot measurement of temperature and pressure using laser-induced thermal gratings with a long probe pulse
Applied Physics B 78 (2004) 111-117
A high power single-mode tunable laser for nonlinear optical diagnostics in combustion
Institute of Physics Conference Series 177 (2003) 61
Abstract:
Nonlinear optical techniques for combustion diagnostics place stringent demands on the lasers employed. High resolution techniques require narrow bandwidth, preferably single longitudinal mode (SLM), combined with wide tunability and high power. A particular aim of our work is to provide a suitable device for nonlinear optical spectroscopy in the mid-infra-red for diagnostics of hydrocarbon radicals. We report the development of a laser device with the desired properties and its application to high resolution spectroscopy of combustion species. The system is based on a modeless laser used as a narrow bandwidth amplifier (NBA) of radiation from a widely tunable, SLM, diode laser. When pumped by 200 mJ of energy from a frequency doubled, SLM, Nd:Yag laser the system provides output pulses of up to 30 mJ energy in a transform limited bandwidth of <200 MHz, or 0.006 cm-1. The single mode frequency is continuously tunable over the diode range of 10 nm. Application of the system to combustion diagnostics is demonstrated by high resolution DFWM spectroscopy of OH in a methane/air flame. Resolution of the spectral lineshape is shown to distinguish effects of Doppler and homogeneous broadening. Applications of the system to other spectroscopic techniques and spectral regions will be reported. © 2003 IOP Publishing Ltd.Optical diagnostics of pressure and temperature using laser induced thermal gratings
Institute of Physics Conference Series 177 (2003) 95
Abstract:
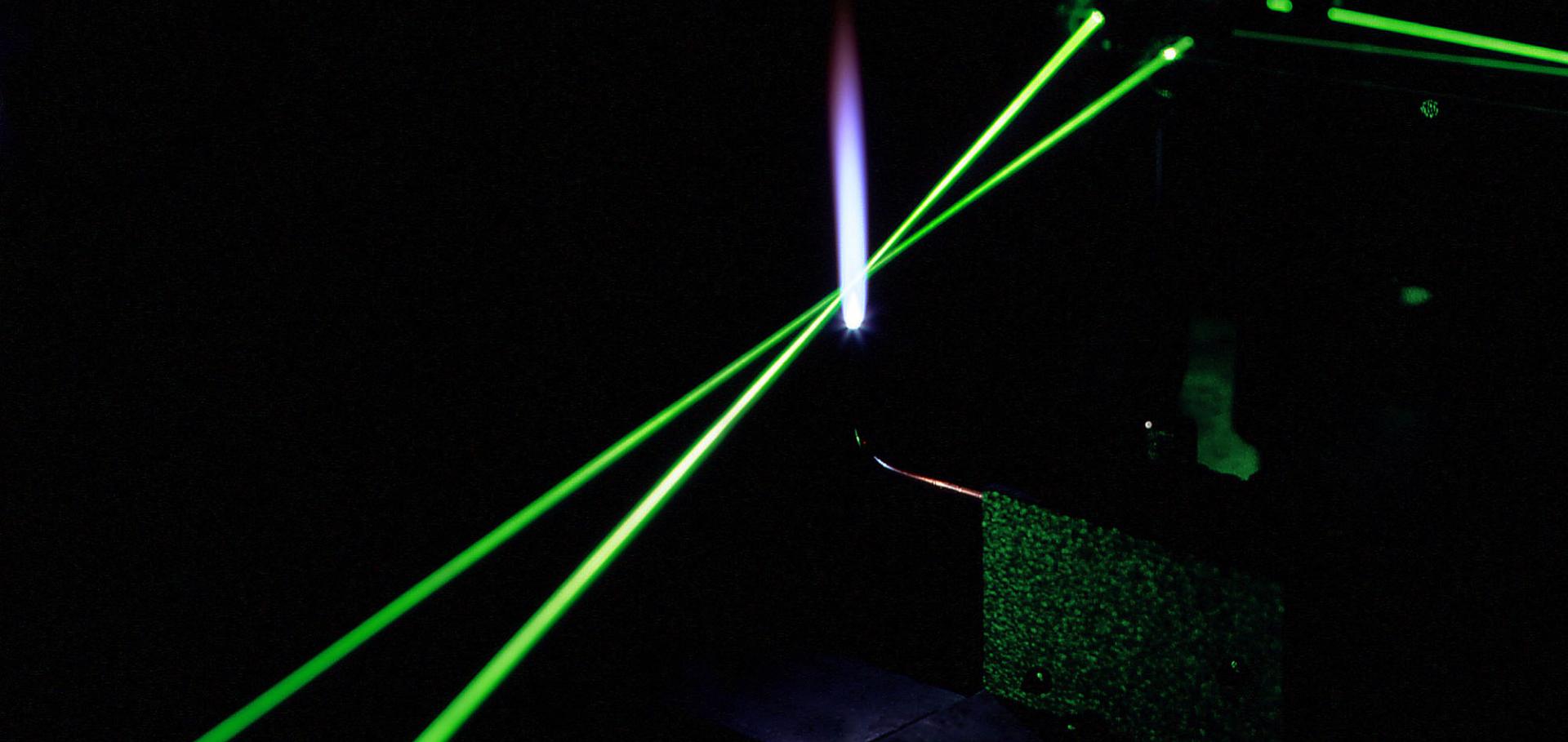
Laser induced thermal grating spectroscopy (LITGS) is based on scattering from gratings produced by interference in a resonantly absorbing gas, of two pump laser beams crossing at a small angle. Interference between a stationary temperature grating and induced acoustic waves leads to a modulation of the grating scattering efficiency. The dynamics of the grating evolution and decay may be monitored by scattering of a probe beam incident at the appropriate Bragg angle. Previous studies have used cw probe lasers with power of approximately 1 W and so the scattered signals are limited by the energy incident during a grating lifetime of typically 0.1 to 1.0 μsec. In the present work we demonstrate the use of long pulse probes (pulse duration 1.5 μsec) with powers of up to 1 MW yielding a potential dramatic increase in detection sensitivity. LITGS in NO2 in buffer gas pressures from 1 to 40 bar are detected in concentrations down to 100 ppm. Simulations, based on linearized hydrodynamic equations, fitted to the data allow accurate time and space resolved measurements of temperature and pressure. Applications to other species of combustion interest, flame and engine measurements will be discussed. © 2003 IOP Publishing Ltd.Saturation effects in molecular spectroscopy using degenerate four-wave mixing
J RAMAN SPECTROSC 34:12 (2003) 1030-1036