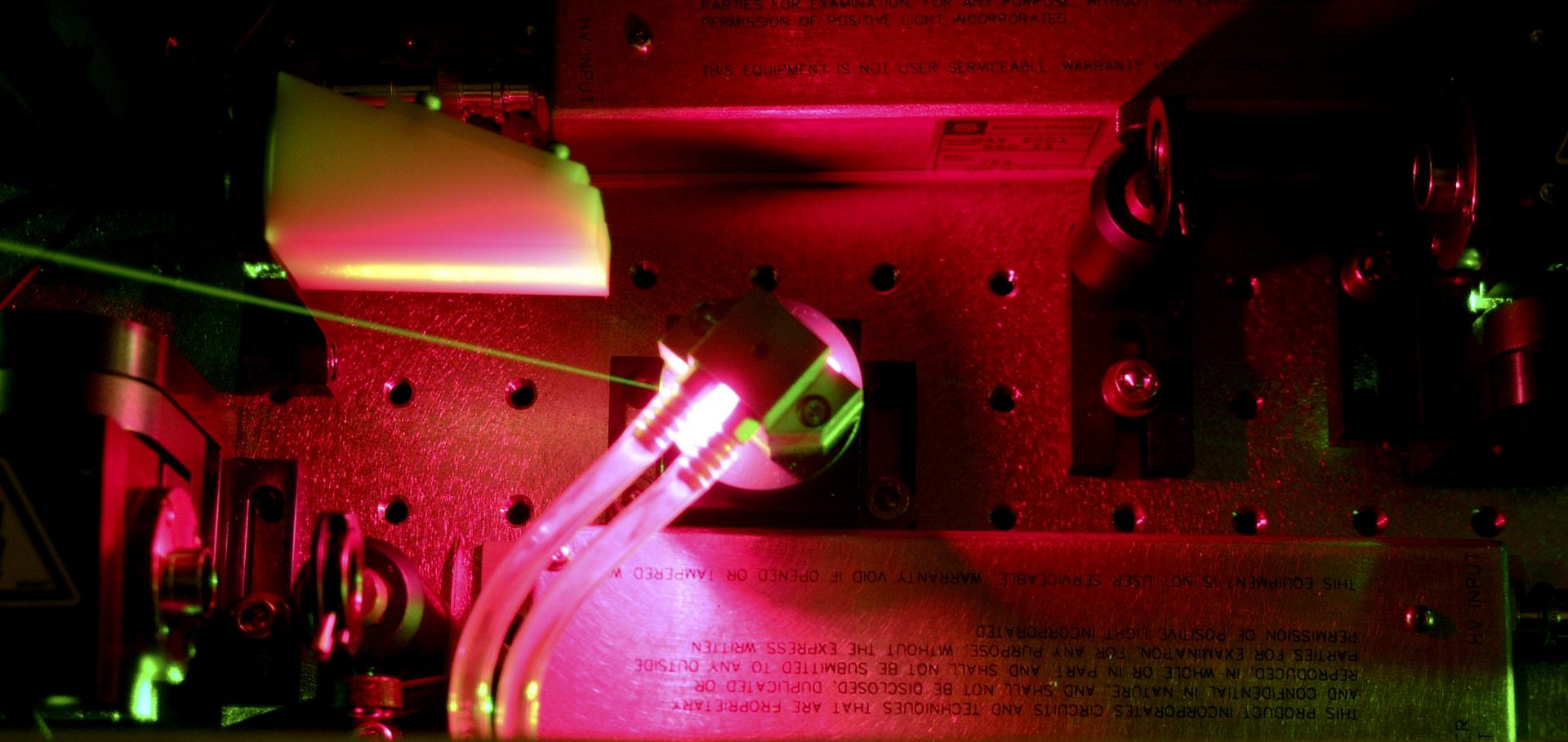
A compact, low cost Marx bank for generating capillary discharge plasmas
Review of Scientific Instruments AIP Publishing 87:093302 (2016)
Abstract:
We describe in detail a low power Compact Marx Bank (CMB) circuit that can provide 20 kV, 500A pulses of approximately 100–200 ns duration. One application is the generation of capillary discharge plasmas of density ≈ 1018 cm3 used in laser plasma accelerators. The CMB is tiggered with a high speed solid state switch and gives a HV output pulse with a ns scale rise time into a 50Ω load (coaxial cable) with < 4 ns voltage jitter. Its small size (10 cm × 25 cm × 5 cm) means that it can be placed right next to the capillary discharge in the target chamber so avoiding the need to impedance match. The electrical energy required per discharge is < 1 J and the CMB can be run at shot repetition rates of >∼ 1 Hz. This low power requirement means the circuit can easily be powered by a small lead acid battery and so therefore can be floated relative to laboratory earth. The CMB is readily scalable and pulses > 45 kV are demonstrated in air discharges.Gaussian-Schell analysis of the transverse spatial properties of high-harmonic beams
(2016)
X-ray characterisation by energy-resolved powder diffraction
Physical Review Accelerators and Beams American Physical Society 19 (2016) 082801
Abstract:
A method for single-shot, non-destructive characterisation of broadband X-ray beams, based on energy-resolved powder diffraction, is described. Monte-Carlo simulations are used to simulate data for X-ray beams in the keV range with parameters similar to those generated by betatron oscillations in a laser-driven plasma accelerator. The retrieved X-ray spectra are found to be in excellent agreement with those of the input beams for realistic numbers of incident photons. It is demonstrated that the angular divergence of the X-rays can be deduced from the deviation of the detected photons from the Debye-Scherrer rings which would be produced by a parallel beam. It is shown that the angular divergence can be measured as a function of the photon energy, yielding the angularly-resolved spectrum of the input X-ray beam.Gaussian-Schell analysis of the transverse spatial properties of high-harmonic beams
Scientific Reports Nature Publishing Group 6 (2016) 30504
Abstract:
High harmonic generation (HHG) is an established means of producing coherent, short wavelength, ultrafast pulses from a compact set-up. Table-top high-harmonic sources are increasingly being used to image physical and biological systems using emerging techniques such as coherent diffraction imaging and ptychography. These novel imaging methods require coherent illumination, and it is therefore important to both characterize the spatial coherence of high-harmonic beams and understand the processes which limit this property. Here we investigate the near- and far-field spatial properties of high-harmonic radiation generated in a gas cell. The variation with harmonic order of the intensity profile, wavefront curvature, and complex coherence factor is measured in the far-field by the SCIMITAR technique. Using the Gaussian-Schell model, the properties of the harmonic beam in the plane of generation are deduced. Our results show that the order-dependence of the harmonic spatial coherence is consistent with partial coherence induced by both variation of the intensity-dependent dipole phase as well as finite spatial coherence of the driving radiation. These findings are used to suggest ways in which the coherence of harmonic beams could be increased further, which would have direct benefits to imaging with high-harmonic radiation.Electron bunch profile reconstruction based on phase-constrained iterative algorithm
Physical Review Accelerators and Beams American Physical Society 19:3 (2016)