Real-Time Observation of Aharonov-Bohm Interference in a $\mathbb{Z}_2$ Lattice Gauge Theory on a Hybrid Qubit-Oscillator Quantum Computer
(2025)
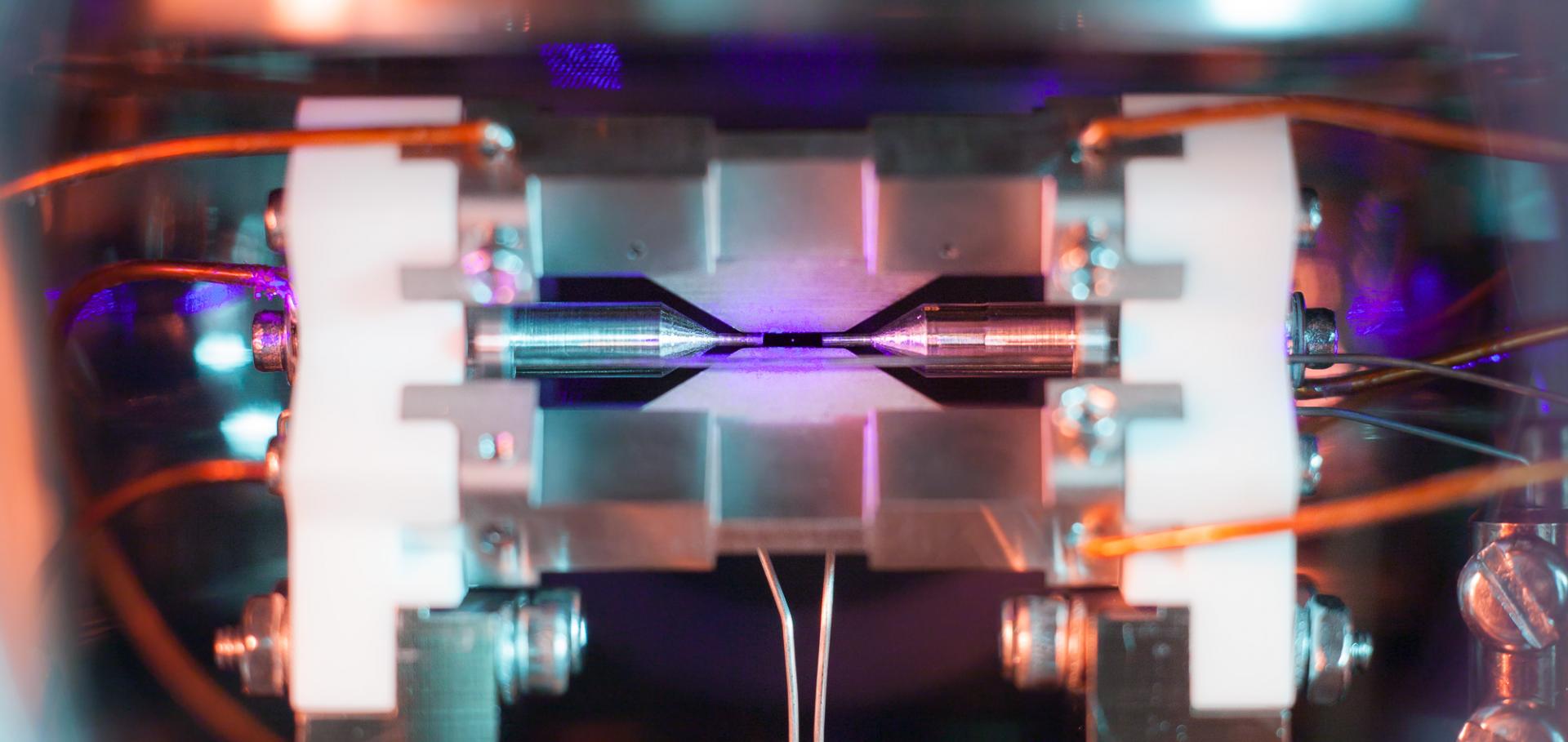
Multipartite Mixed-Species Entanglement over a Quantum Network
(2025)
Single-Qubit Gates with Errors at the 10-7 Level
Physical Review Letters American Physical Society (APS) 134:23 (2025) 230601
Experimental quantum advantage in the odd-cycle game
Physical Review Letters American Physical Society 134 (2025) 070201
Abstract:
We report the first experimental demonstration of the odd-cycle game. We entangle two atoms separated by ∼ 2 m and the players use them to win the odd-cycle game with a probability ∼ 26σ above that allowed by the best classical strategy. The experiment implements the optimal quantum strategy, is free of loopholes, and achieves 97.8(3) % of the theoretical limit to the quantum winning probability. We perform the associated Bell test and measure a nonlocal content of 0.54(2) – the largest value for physically separate devices, free of the detection loophole, ever observed.
Distributed quantum computing across an optical network link
Nature Nature Research 638:8050 (2025) 383-388