The HETDEX Instrumentation: Hobby-Eberly Telescope Wide Field Upgrade and VIRUS
(2021)
The Hobby-Eberly Telescope Dark Energy Experiment (HETDEX) Survey Design, Reductions, and Detections
(2021)
Wide-Field Near Infrared Imaging
Chapter in , World Scientific Publishing (2021) 175-185
MOSAIC on the ELT: high-multiplex spectroscopy to unravel the physics of stars and galaxies from the dark ages to the present-day
The ESO Messenger (2021)
Abstract:
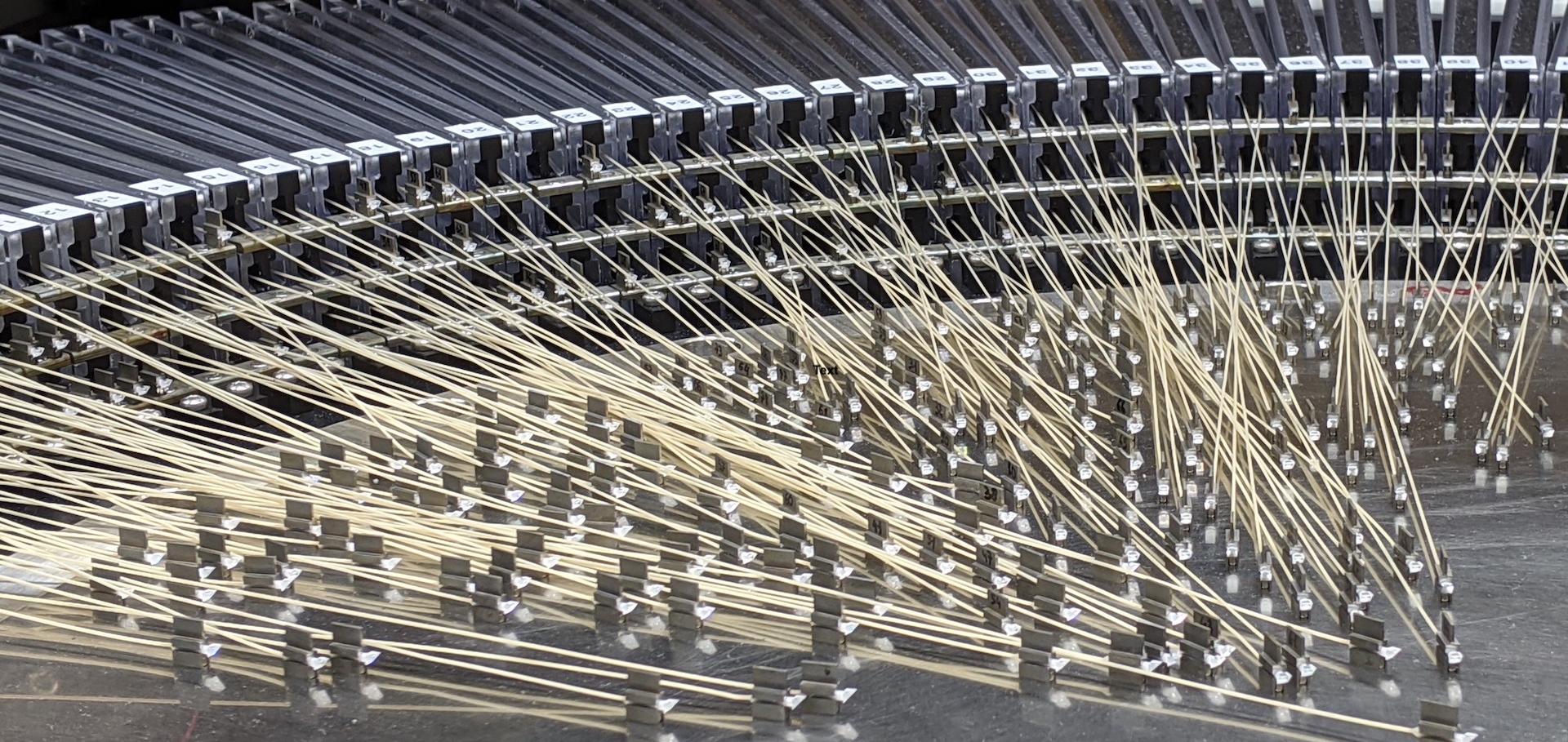
The powerful combination of the cutting-edge multi-object spectrograph MOSAIC with the world largest telescope, the ELT, will allow us to probe deeper into the Universe than was possible. MOSAIC is an extremely efficient instrument in providing spectra for the numerous faint sources in the Universe, including the very first galaxies and sources of cosmic reionization. MOSAIC has a high multiplex in the NIR and in the VIS, in addition to multi-Integral Field Units (Multi-IFUs) in NIR. As such it is perfectly suited to carry out an inventory of dark matter (from rotation curves) and baryons in the cool-warm gas phases in galactic haloes at z=3-4. MOSAIC will enable detailed maps of the intergalactic medium at z=3, the evolutionary history of dwarf galaxies during a Hubble time, the chemistry directly measured from stars up to several Mpc. Finally, it will measure all faint features seen in cluster gravitational lenses or in streams surrounding nearby galactic halos, providing MOSAIC to be a powerful instrument with an extremely large space of discoveries. The preliminary design of MOSAIC is expected to begin next year, and its level of readiness is already high, given the instrumental studies made by the team.Fibre links for the WEAVE instrument: the making of
Society of Photo-optical Instrumentation Engineers (2020) 114502F