A piperidinium salt stabilizes efficient metal-halide perovskite solar cells.
Science (New York, N.Y.) Nature Research 369:6499 (2020) 96-102
Abstract:
Longevity has been a long-standing concern for hybrid perovskite photovoltaics. We demonstrate high-resilience positive-intrinsic-negative perovskite solar cells by incorporating a piperidinium-based ionic compound into the formamidinium-cesium lead-trihalide perovskite absorber. With the bandgap tuned to be well suited for perovskite-on-silicon tandem cells, this piperidinium additive enhances the open-circuit voltage and cell efficiency. This additive also retards compositional segregation into impurity phases and pinhole formation in the perovskite absorber layer during aggressive aging. Under full-spectrum simulated sunlight in ambient atmosphere, our unencapsulated and encapsulated cells retain 80 and 95% of their peak and post-burn-in efficiencies for 1010 and 1200 hours at 60° and 85°C, respectively. Our analysis reveals detailed degradation routes that contribute to the failure of aged cells.Metal composition influences optoelectronic quality in mixed-metal lead-tin triiodide perovskite solar absorbers
Energy and Environmental Science Royal Society of Chemistry 13:6 (2020) 1776-1787
Abstract:
Current designs for all-perovskite multi-junction solar cells require mixed-metal Pb-Sn compositions to achieve narrower band gaps than are possible with their neat Pb counterparts. The lower band gap range achievable with mixed-metal Pb-Sn perovskites also encompasses the 1.3 to 1.4 eV range that is theoretically ideal for maximising the efficiency of single-junction devices. Here we examine the optoelectronic quality and photovoltaic performance of the ((HC(NH2)2)0.83Cs0.17)(Pb1-ySny)I3 family of perovskite materials across the full range of achievable band gaps by substituting between 0.001% and 70% of the Pb content with Sn. We reveal that a compositional range of "defectiveness"exists when Sn comprises between 0.5% and 20% of the metal content, but that the optoelectronic quality is restored for Sn content between 30-50%. When only 1% of Pb content is replaced by Sn, we find that photoconductivity, photoluminescence lifetime, and photoluminescence quantum efficiency are reduced by at least an order of magnitude, which reveals that a small concentration of Sn incorporation produces trap sites that promote non-radiative recombination in the material and limit photovoltaic performance. While these observations suggest that band gaps between 1.35 and 1.5 eV are unlikely to be useful for optoelectronic applications without countermeasures to improve material quality, highly efficient narrower band gap absorber materials are possible at or below 1.33 eV. Through optimising single-junction photovoltaic devices with Sn compositions of 30% and 50%, we respectively demonstrate a 17.6% efficient solar cell with an ideal single-junction band gap of 1.33 eV and an 18.1% efficient low band gap device suitable for the bottom absorber in all-perovskite multi-junction cells.Three-dimensional cross-nanowire networks recover full terahertz state
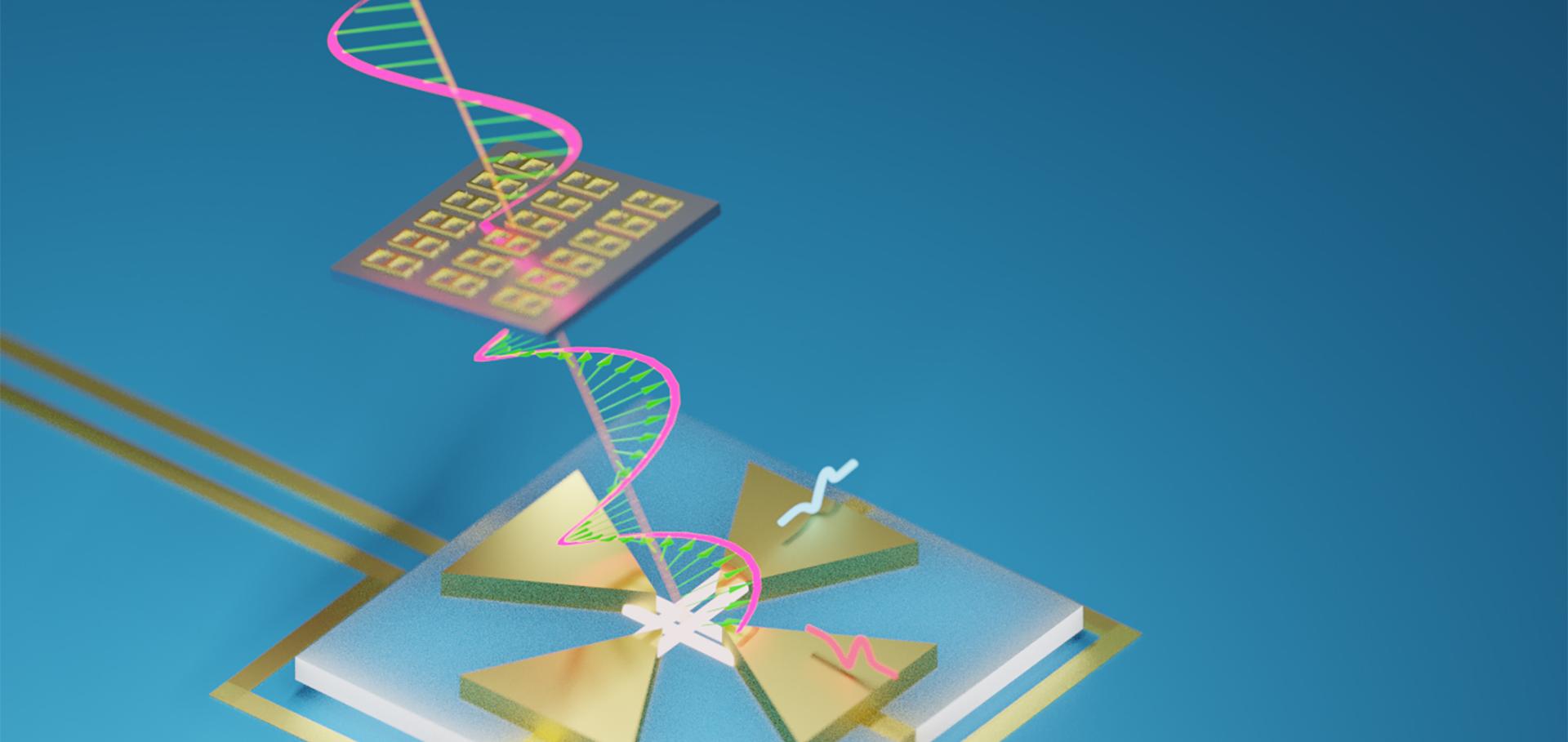
Science American Association for the Advancement of Science 368:6490 (2020) 510-513
Abstract:
Terahertz radiation encompasses a wide band of the electromagnetic spectrum, spanning from microwaves to infrared light, and is a particularly powerful tool for both fundamental scientific research and applications such as security screening, communications, quality control, and medical imaging. Considerable information can be conveyed by the full polarization state of terahertz light, yet to date, most time-domain terahertz detectors are sensitive to just one polarization component. Here we demonstrate a nanotechnology-based semiconductor detector using cross-nanowire networks that records the full polarization state of terahertz pulses. The monolithic device allows simultaneous measurements of the orthogonal components of the terahertz electric field vector without cross-talk. Furthermore, we demonstrate the capabilities of the detector for the study of metamaterials.Three-dimensional cross-nanowire networks recover full terahertz state.
Science (New York, N.Y.) 368:6490 (2020) 510-513
Abstract:
Terahertz radiation encompasses a wide band of the electromagnetic spectrum, spanning from microwaves to infrared light, and is a particularly powerful tool for both fundamental scientific research and applications such as security screening, communications, quality control, and medical imaging. Considerable information can be conveyed by the full polarization state of terahertz light, yet to date, most time-domain terahertz detectors are sensitive to just one polarization component. Here we demonstrate a nanotechnology-based semiconductor detector using cross-nanowire networks that records the full polarization state of terahertz pulses. The monolithic device allows simultaneous measurements of the orthogonal components of the terahertz electric field vector without cross-talk. Furthermore, we demonstrate the capabilities of the detector for the study of metamaterials.Charge-carrier trapping dynamics in bismuth-doped thin films of MAPbBr3 perovskite
Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters American Chemical Society 11:9 (2020) 3681-3688