Reduction of heating rate in a microfabricated ion trap by pulsed-laser cleaning
(2011)
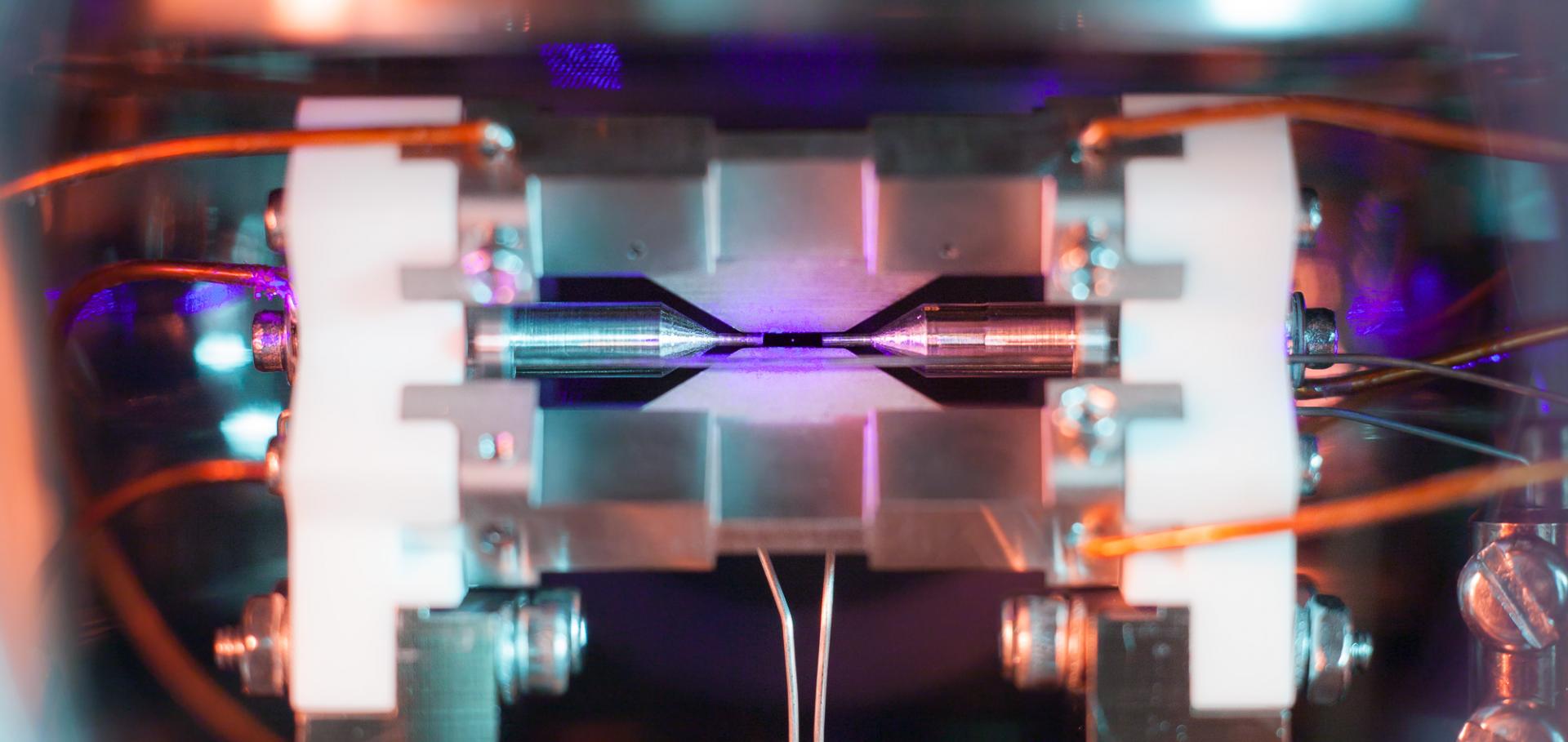
Heating rate and electrode charging measurements in a scalable, microfabricated, surface-electrode ion trap
ArXiv (2011)
Abstract:
We characterise the performance of a surface-electrode ion "chip" trap fabricated using established semiconductor integrated circuit and micro-electro-mechanical-system (MEMS) microfabrication processes which are in principle scalable to much larger ion trap arrays, as proposed for implementing ion trap quantum information processing. We measure rf ion micromotion parallel and perpendicular to the plane of the trap electrodes, and find that on-package capacitors reduce this to <~ 10 nm in amplitude. We also measure ion trapping lifetime, charging effects due to laser light incident on the trap electrodes, and the heating rate for a single trapped ion. The performance of this trap is found to be comparable with others of the same size scale.Heating rate and electrode charging measurements in a scalable, microfabricated, surface-electrode ion trap
(2011)
Keeping a single qubit alive by experimental dynamic decoupling
Journal of Physics B: Atomic, Molecular and Optical Physics 44:2 (2011)