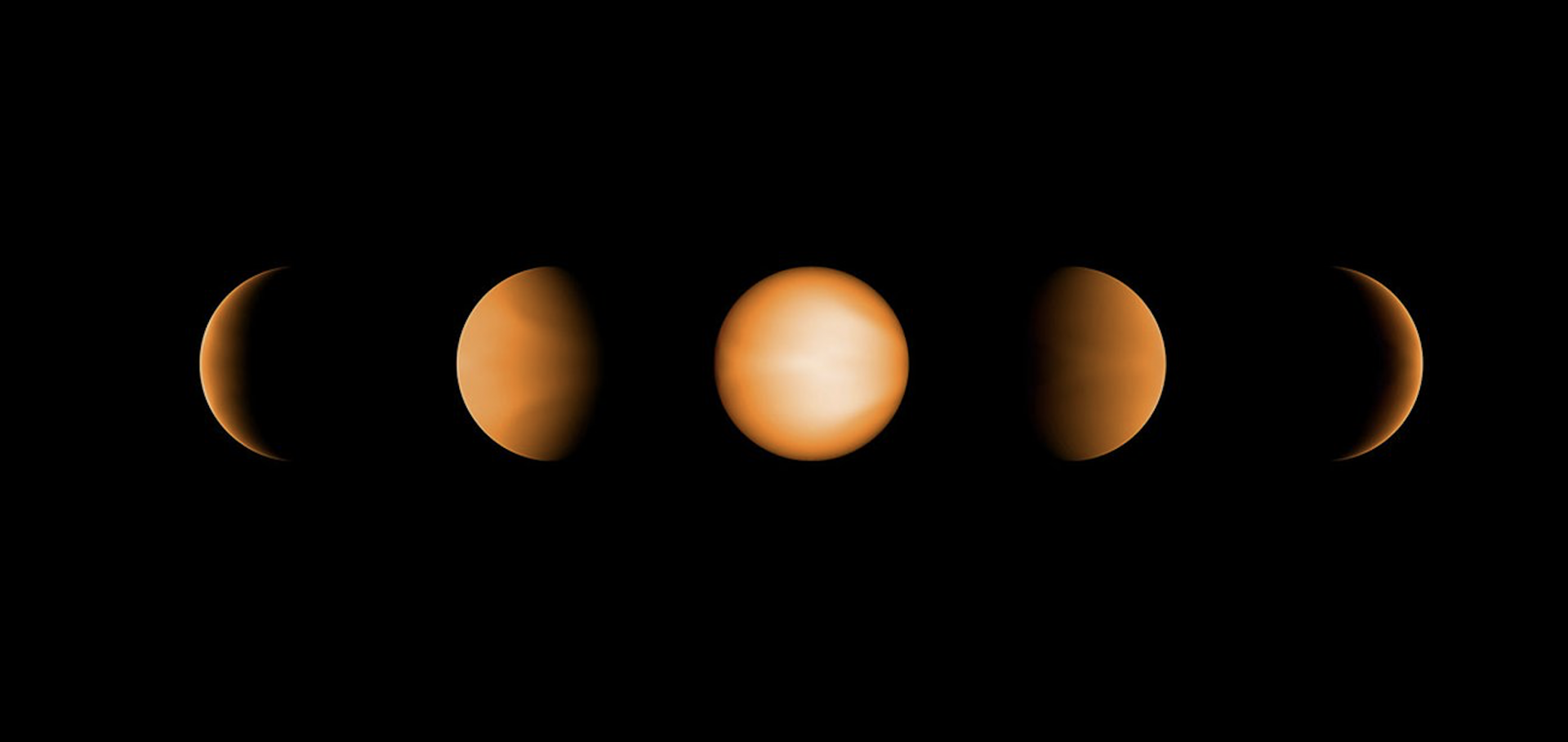
A benchmark JWST near-infrared spectrum for the exoplanet WASP-39 b
Nature Astronomy Nature Research 8:8 (2024) 1008-1019
Abstract:
Observing exoplanets through transmission spectroscopy supplies detailed information about their atmospheric composition, physics and chemistry. Before the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST), these observations were limited to a narrow wavelength range across the near-ultraviolet to near-infrared, alongside broadband photometry at longer wavelengths. To understand more complex properties of exoplanet atmospheres, improved wavelength coverage and resolution are necessary to robustly quantify the influence of a broader range of absorbing molecular species. Here we present a combined analysis of JWST transmission spectroscopy across four different instrumental modes spanning 0.5–5.2 μm using Early Release Science observations of the Saturn-mass exoplanet WASP-39 b. Our uniform analysis constrains the orbital and stellar parameters within subpercentage precision, including matching the precision obtained by the most precise asteroseismology measurements of stellar density to date, and it further confirms the presence of Na, K, H2O, CO, CO2 and SO2 as atmospheric absorbers. Through this process, we have improved the agreement between the transmission spectra of all modes, except for the NIRSpec PRISM, which is affected by partial saturation of the detector. This work provides strong evidence that uniform light curve analysis is an important aspect to ensuring reliability when comparing the high-precision transmission spectra provided by JWST.Sulfur Dioxide and Other Molecular Species in the Atmosphere of the Sub-Neptune GJ 3470 b
The Astrophysical Journal Letters American Astronomical Society 970:1 (2024) l10
Atmospherix
Astronomy & Astrophysics EDP Sciences 687 (2024) a119
A high internal heat flux and large core in a warm Neptune exoplanet
Nature Springer Nature 630:8018 (2024) 836-840
Simultaneous retrieval of orbital phase resolved JWST/MIRI emission spectra of the hot Jupiter WASP-43b: evidence of water, ammonia and carbon monoxide
Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society Oxford University Press 532:1 (2024) 460-475