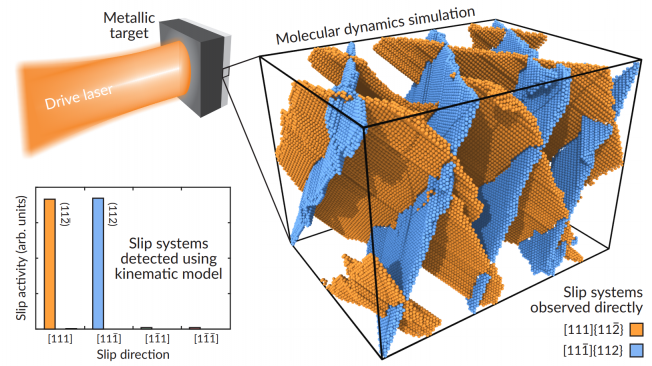
Shock-driven amorphization and melting in
Physical Review B (condensed matter and materials physics) American Physical Society 111:2 (2025) 24209
Abstract:
<jats:p>We present measurements on <a:math xmlns:a="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"><a:mrow><a:msub><a:mi>Fe</a:mi><a:mn>2</a:mn></a:msub><a:msub><a:mi mathvariant="normal">O</a:mi><a:mn>3</a:mn></a:msub></a:mrow></a:math> amorphization and melt under laser-driven shock compression up to 209(10) GPa via time-resolved x-ray diffraction. At 122(3) GPa, a diffuse signal is observed indicating the presence of a noncrystalline phase. Structure factors have been extracted up to 182(6) GPa showing the presence of two well-defined peaks. A rapid change in the intensity ratio of the two peaks is identified between 145(12) and 151(12) GPa, indicative of a phase change. The noncrystalline diffuse scattering is consistent with shock amorphization of <c:math xmlns:c="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"><c:mrow><c:msub><c:mi>Fe</c:mi><c:mn>2</c:mn></c:msub><c:msub><c:mi mathvariant="normal">O</c:mi><c:mn>3</c:mn></c:msub></c:mrow></c:math> between 122(3) and 145(12) GPa, followed by an amorphous-to-liquid transition above 151(12) GPa. Upon release, a noncrystalline phase is observed alongside crystalline <e:math xmlns:e="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"><e:mrow><e:mi>α</e:mi><e:mtext>−</e:mtext><e:msub><e:mi>Fe</e:mi><e:mn>2</e:mn></e:msub><e:msub><e:mi mathvariant="normal">O</e:mi><e:mn>3</e:mn></e:msub></e:mrow></e:math>. The extracted structure factor and pair distribution function of this release phase resemble those reported for <g:math xmlns:g="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"><g:mrow><g:msub><g:mi>Fe</g:mi><g:mn>2</g:mn></g:msub><g:msub><g:mi mathvariant="normal">O</g:mi><g:mn>3</g:mn></g:msub></g:mrow></g:math> melt at ambient pressure.</jats:p> <jats:sec> <jats:title/> <jats:supplementary-material> <jats:permissions> <jats:copyright-statement>Published by the American Physical Society</jats:copyright-statement> <jats:copyright-year>2025</jats:copyright-year> </jats:permissions> </jats:supplementary-material> </jats:sec>Femtosecond temperature measurements of laser-shocked copper deduced from the intensity of the x-ray thermal diffuse scattering
(2025)
Unexpected Observation of Disorder and Multiple Phase-Transition Pathways in Shock-Compressed Zr
Physical Review Letters American Physical Society (APS) 133:9 (2024) 096101
Diffuse scattering from dynamically compressed single-crystal zirconium following the pressure-induced
α → ω
Physical Review B American Physical Society (APS) 110:5 (2024) 054113
Abstract:
Resonant inelastic x-ray scattering in warm-dense Fe compounds beyond the SASE FEL resolution limit
Communications Physics Nature Research 7:1 (2024) 266