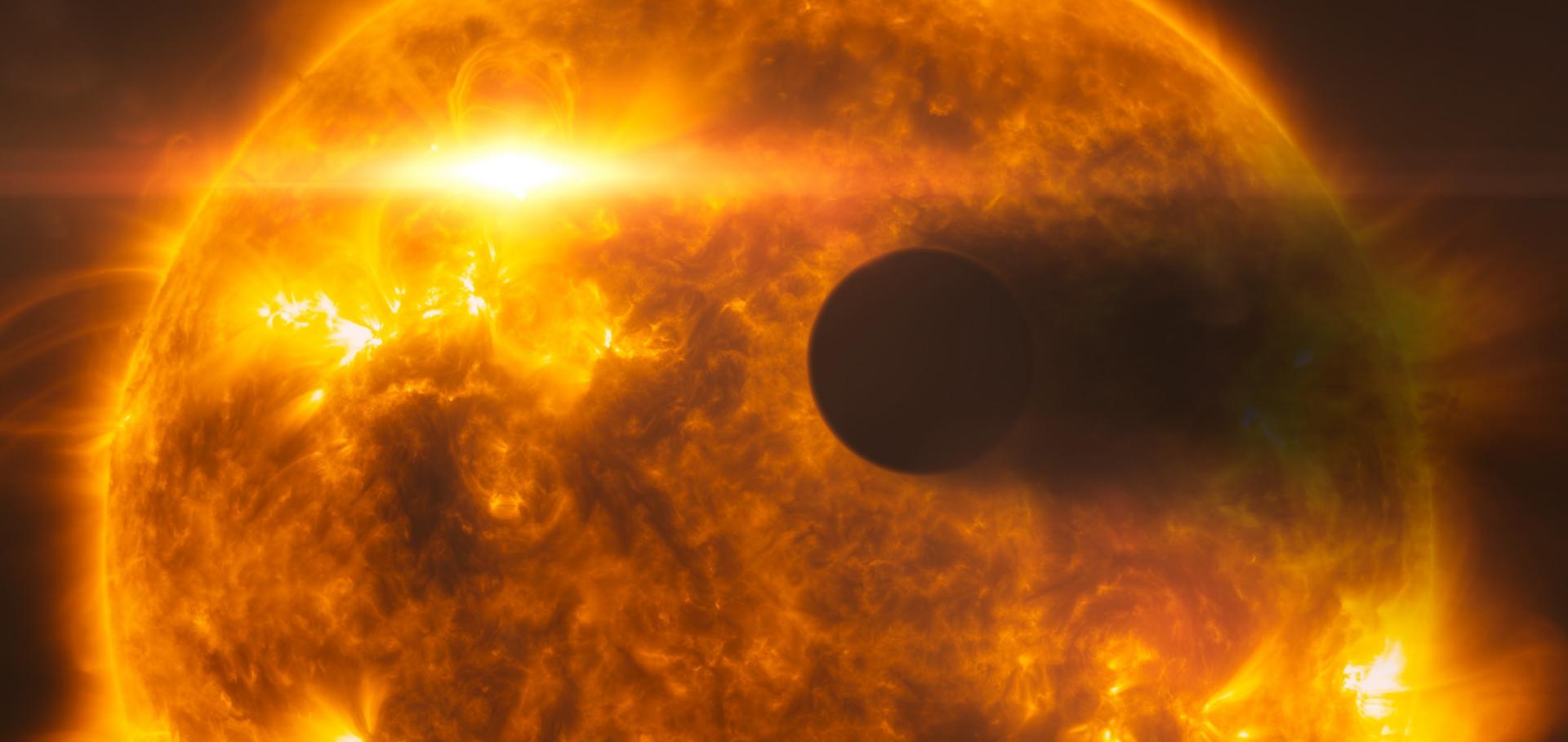
The young HD 73583 (TOI-560) planetary system: Two 10-M$_\oplus$ mini-Neptunes transiting a 500-Myr-old, bright, and active K dwarf
(2021)
The search for living worlds and the connection to our cosmic origins
Experimental Astronomy Springer 54:2-3 (2021) 1275-1306
Abstract:
One of the most exciting scientific challenges is to detect Earth-like planets in the habitable zones of other stars in the galaxy and search for evidence of life. During the past 20 years the detection of exoplanets, orbiting stars beyond our own, has moved from science fiction to science fact. From the first handful of gas giants, found through radial velocity studies, detection techniques have increased in sensitivity, finding smaller planets and diverse multi-planet systems. Through enhanced ground-based spectroscopic observations, transit detection techniques and the enormous productivity of the Kepler space mission, the number of confirmed planets has increased to more than 2000. Several space missions, including TESS (NASA), now operational, and PLATO (ESA), will extend the parameter space for exoplanet discovery towards the regime of rocky Earth-like planets and take the census of such bodies in the neighbourhood of the Solar System. The ability to observe and characterise dozens of potentially rocky Earth-like planets now lies within the realm of possibility due to rapid advances in key space and imaging technologies and active studies of potential missions have been underway for a number of years. The latest of these is the Large UV Optical IR space telescope (LUVOIR), one of four flagship mission studies commissioned by NASA in support of the 2020 US Decadal Survey. LUVOIR, if selected, will be of interest to a wide scientific community and will be the only telescope capable of searching for and characterizing a sufficient number of exo-Earths to provide a meaningful answer to the question “Are we alone?”. This contribution is a White Paper that has been submitted in response to the ESA Voyage 2050 Call.PYANETI II: a multi-dimensional Gaussian process approach to analysing spectroscopic time-series
Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society Oxford University Press 509:1 (2021) 866-883
Abstract:
The two most successful methods for exoplanet detection rely on the detection of planetary signals in photometric and radial velocity time-series. This depends on numerical techniques that exploit the synergy between data and theory to estimate planetary, orbital, and/or stellar parameters. In this work we present a new version of the exoplanet modelling code pyaneti. This new release has a special emphasis on the modelling of stellar signals in radial velocity time-series. The code has a built-in multi-dimensional Gaussian process approach to modelling radial velocity and activity indicator time-series with different underlying covariance functions. This new version of the code also allows multi-band and single transit modelling; it runs on Python 3, and features overall improvements in performance. We describe the new implementation and provide tests to validate the new routines that have direct application to exoplanet detection and characterisation. We have made the code public and freely available at https://github.com/oscaribv/pyaneti. We also present the codes citlalicue and citlalatonac that allow one to create synthetic photometric and spectroscopic time-series, respectively, with planetary and stellar-like signals.pyaneti II: A multidimensional Gaussian process approach to analysing spectroscopic time-series
(2021)
A HARPS-N mass for the elusive Kepler-37d: a case study in disentangling stellar activity and planetary signals
Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society Oxford University Press 507:2 (2021) 1847-1868