Comprehensive Analysis of Temperature-Dependent Photoluminescence in Silica-Encapsulated CsPbBr3 and CsPbI3 Perovskite Nanocrystals
Nanomaterials MDPI 16:1 (2026) 76
Abstract:
The temperature-dependent photoluminescence of CsPbBr3/SiO2 and CsPbI3/SiO2 nanocrystals was investigated to understand the thermal stability of SiO2 encapsulation. At increased temperature, intensity quenching, linewidth broadening, energy level shift, and decay dynamics were evaluated as quantified parameters. Comprehensive analysis of these parameters supports that CsPbI3/SiO2 nanocrystals show a stronger interaction with phonons compared with CsPbBr3/SiO2 nanocrystals. Despite SiO2 encapsulation, we conclude that trapping states are still present and the degree of localization can be characterized in terms of short-lived decay time and thermal activation energy.Dispersive near-infrared metalens integrated with linear polarization filtering functionality
Results in Optics Elsevier 21:Appl. Phys. Lett. 124 24 2024 (2025) 100902
Abstract:
The miniaturization and enhanced functionality of LiDAR systems present critical challenges in automotive sensing technologies, particularly in achieving efficient wide-angle beam scanning while maintaining compact form factors. We demonstrate a novel dual-wavelength polarization-selective concave metalens operating at 904 nm and 940 nm wavelengths, the standard operating wavelengths for LiDAR systems. By engineering rectangular TiO2 nanopillars on a quartz substrate, we achieved simultaneous polarization filtering and concave phase profile functionality within a single metasurface layer. The optimized 600 nm × 600 nm unit cell design with 1.7 μm height nanopillars enables full 2π phase coverage while maintaining high transmission efficiency for the desired polarization state. Our fabricated metalens exhibits remarkable polarization extinction ratios (ER) of 124:1 and 102:1 at 904 nm and 940 nm wavelengths, respectively. Angular-resolved measurements demonstrate wide beam divergence angles of 148° and 138° at the respective wavelengths, with 50 % of total power contained within ± 38° and ± 25°.Narrow Linewidth Spontaneous and Lasing Emissions from Open‐Access Microcavity‐Embedded Perovskite Quantum Dots
Advanced Optical Materials Wiley (2025) e01918
Abstract:
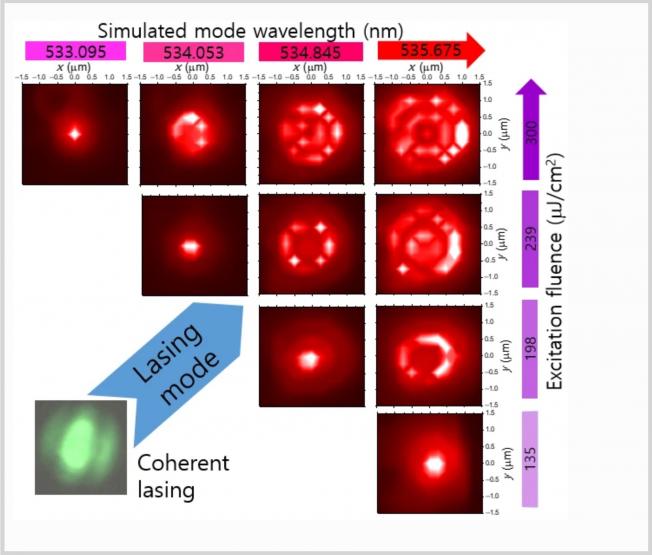
Achieving efficient optical coupling between the emission from perovskite quantum dots (PQDs) and photonic integrated elements requires ultranarrow linewidths and highly directional emission. These are challenging goals at room temperature due to the broad and isotropic nature of perovskite emission. Here, we demonstrate ultranarrow‐linewidth emission from CsPbBr3 PQDs at room temperature, in both spontaneous and stimulated regimes, by coupling to state‐of‐the‐art open‐access curved dielectric cavities under continuous wave excitation. The emission is confined to a single transverse electromagnetic mode of the cavity, achieving a remarkably narrow linewidth of 0.2 nm, ≈100× narrower than free‐space emission in both the emission regime. Single‐mode lasing from a small number of PQDs is observed, yielding a quality factor of ≈2590, among the highest reported for single‐mode lasing. The open‐access design enables precise tuning of cavity length and selective coupling of emitters in their native state, overcoming the limitations associated with closed and fixed‐length vertical‐cavity surface emitting laser geometries. The geometry's low divergence and tunability provide an efficient route for integrating perovskite emitters with on‐chip photonic circuits, advancing their use in quantum and optoelectronic technologies.Nanoscale MoS 2 -in-Nanoporous Au Hybrid Structure for Enhancing Electrochemical Sensing
Sensors MDPI 25:23 (2025) 7137
Abstract:
We report the fabrication of nanoscale MoS2 (nMoS2) via laser ablation in liquid and its application in electrochemical sensing. The laser ablation process fragments microscale MoS2 sheets into ~5 nm dots with stable aqueous dispersibility. Electrochemical analysis reveals that nMoS2 possesses multiple reversible redox states, enabling it to participate in redox cycling reactions that can amplify electrochemical signals. When the nMoS2 is embedded in an electrochemically inert matrix, a chitosan layer, and subsequently incorporated within a nanostructured Au electrode, the nMoS2-participating redox cycling reactions are further enhanced by the nanoconfinement effect, leading to synergistic signal amplification. As a model system, this hybrid nMoS2-in-nanoporous Au electrode demonstrates a 9-fold increase in sensitivity for detecting pyocyanin, a biomarker of Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection, compared with a flat electrode without nMoS2 loading. This study not only elucidates the redox characteristics of laser-fabricated zero-dimensional transition metal dichalcogenides but also presents a strategy to integrate semiconducting nanomaterials with metallic nanostructures for high-performance electrochemical sensing.Humidity-resilient trace hydrogen detection using AuPd-Functionalized zinc oxide nanohybrids on surface-engineered silicon substrate
Chemical Engineering Journal Elsevier 524 (2025) 168945