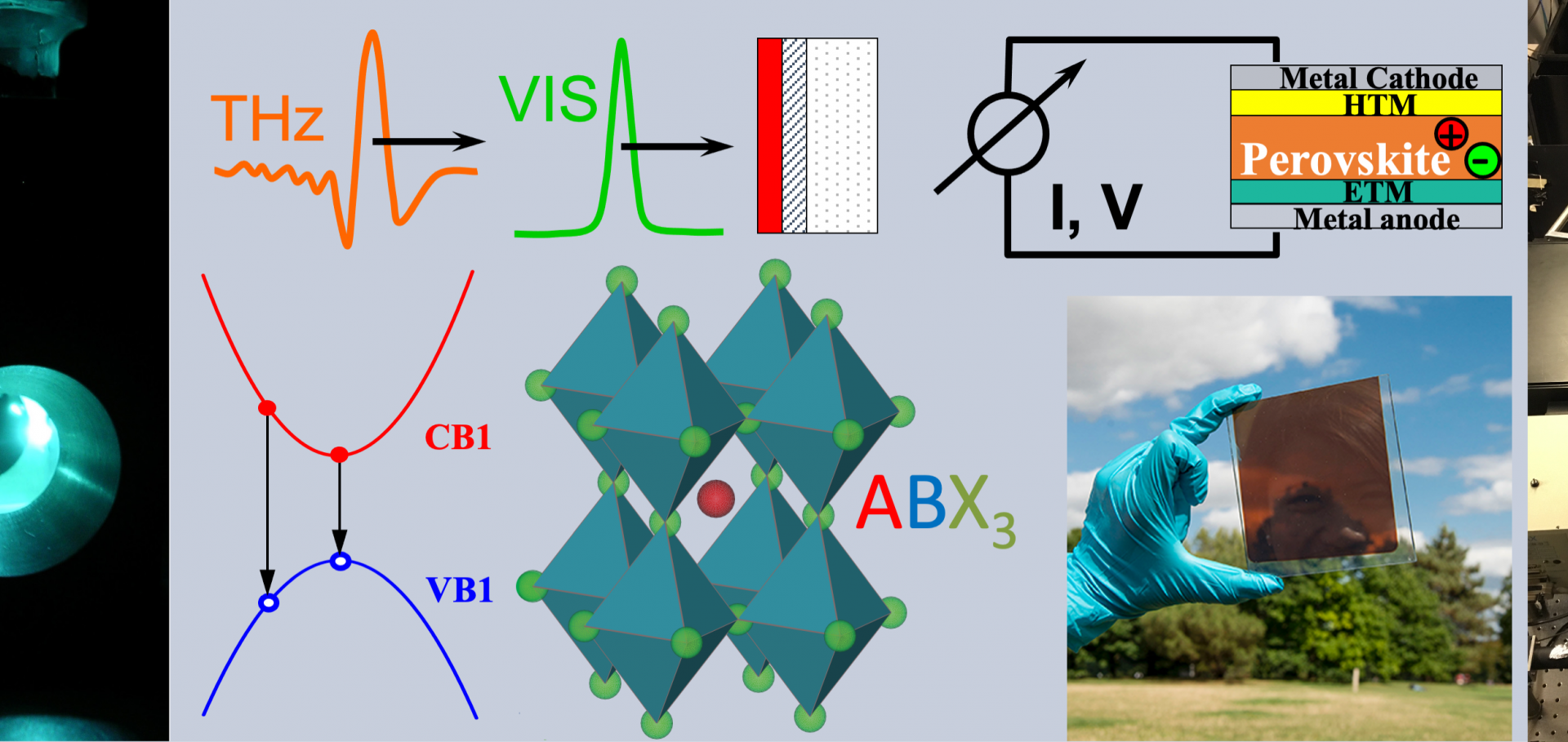
Ruddlesden–Popper Defects Act as a Free Surface: Role in Formation and Photophysical Properties of CsPbI 3
Advanced Materials Wiley (2025) 2501788
Abstract:
The perovskite semiconductor, CsPbI3, holds excellent promise for solar cell applications due to its suitable bandgap. However, achieving phase‐stable CsPbI3 solar cells with high power conversion efficiency remains a major challenge. Ruddlesden–Popper (RP) defects have been identified in a range of perovskite semiconductors, including CsPbI3. However, there is limited understanding as to why they form or their impact on stability and photophysical properties. Here, the prevalence of RP defects is increased with increased Cs‐excess in vapor‐deposited CsPbI3 thin films while superior structural stability but inferior photophysical properties are observed. Significantly, using electron microscopy, it is found that the atomic positions at the planar defect are comparable to those of a free surface, revealing their role in phase stabilization. Density functional theory (DFT) calculations reveal the RP planes are electronically benign, however, antisites observed at RP turning points are likely to be malign. Therefore it is proposed that increasing RP planes while reducing RP turning points offers a breakthrough for improving both phase stability and photophysical performance. The formation mechanism revealed here can apply more generally to RP structures in other perovskite systems.Odd-even effects in lead-iodide-based Ruddlesden–Popper 2D perovskites †
Journal of Materials Chemistry A: materials for energy and sustainability Royal Society of Chemistry (2025)
Abstract:
Two-dimensional (2D) halide perovskites are a versatile material class, exhibiting a layered crystal structure, consisting of inorganic metal–halide sheets separated by organic spacer cations. Unlike their 3D counterparts, 2D perovskites have less strict geometric requirements, allowing for a wider range of molecules to be incorporated. This potentially offers a way to engineer the properties of a 2D perovskite through adequate selection of the organic spacer cations. Our study systematically analyzes the effect of spacer cation length on the electronic and optical properties of Ruddlesden–Popper lead-iodide-based 2D perovskites, using alkylammonium cations of varying chain lengths. Intriguingly, no linear correlation between interlayer distance and the optical gap or valence band position is observed in our measurements. Rather it matters whether the spacer cation contains an odd or even number of carbon atoms in the chain. Notably, these odd-even effects manifest in variations of ionization energy, optical gap as well as charge carrier mobility. Density functional theory calculations reproduce the changes in optical properties, allowing us to identify the underlying mechanism: while even-numbered carbon chains pack efficiently within the organic spacer layer, the shorter odd-numbered chains increase distortions. These distortions lead to variations in the Pb–I–Pb bond angle within the inorganic sheets, resulting in the observed odd-even effect in the (opto-)electronic properties. This understanding will be helpful to make more informed choices regarding the incorporated spacer molecules which can potentially help to enhance performance when integrating such 2D perovskite interlayers into devices.Oriented naphthalene-O-propylammonium-based (NOP)4AuBIIII8 (B = Au, Bi, Sb) Ruddlesden–Popper two-dimensional gold double perovskite thin films featuring high charge-carrier mobility
Journal of the American Chemical Society American Chemical Society 147:20 (2025) 16992-17001
Abstract:
Two-dimensional perovskites show intriguing optoelectronic properties due to their anisotropic structure and multiple quantum well structure. Here, we report the first three gold-based Ruddlesden–Popper type two-dimensional double perovskites with a general formula (NOP)4AuIBIIII8 (B = Au, Bi, Sb) employing naphthalene-O-propylammonium (NOP) as an organic cation. They were found to form highly crystalline thin films on various substrates, predominantly oriented in the [001] direction featuring continuous, crack-free film areas on the μm2 scale. The thin films show strong optical absorption in the visible region, with band gap energies between 1.48 and 2.32 eV. Density functional theory calculations support the experimentally obtained band gap energies and predict high charge-carrier mobilities and effective charge separation. A comprehensive study with time-resolved microwave conductivity (TRMC) and optical-pump-THz-probe (OPTP) spectroscopy revealed high charge-carrier mobilities for lead-free two-dimensional perovskites of 4.0 ± 0.2 cm2(V s)−1 and charge-carrier lifetimes in the range of μs. Photoconductivity measurements under 1 sun illumination demonstrated the material’s application as a photodetector, showing a 2-fold increase in conductivity when exposed to light.Interdiffusion control in sequentially evaporated organic–inorganic perovskite solar cells †
EES Solar Royal Society of Chemistry (2025)
Abstract:
Vacuum deposition of metal halide perovskite is a scalable and adaptable method. In this study, we adopt sequential evaporation to form the perovskite layer and reveal how the relative humidity during the annealing step, impacts its crystallinity and the photoluminescence quantum yield (PLQY). By controlling the humidity, we achieved a significant enhancement of 50 times in PLQY from 0.12% to 6%. This improvement corresponds to an increase in implied open-circuit voltage (Voc) of over 100 meV. We investigate the origin of this enhanced PLQY by combining structural, chemical and spectroscopic methods. Our results show that annealing in a controlled humid environment improves the organic and inorganic halides' interdiffusion throughout the bulk, which in turn significantly reduces non-radiative recombination both in the bulk and at the interfaces with the charge transport layers, which enhanced both the attainable open-circuit voltage and the charge carrier diffusion length. We further demonstrate that the enhanced intermixing results in fully vacuum-deposited FA0.85Cs0.15Pb(IxCl1−x)3 p-i-n perovskite solar cells (PSCs) with a maximum power point tracked efficiency of 21.0% under simulated air mass (AM) 1.5G 100 mW cm−2 irradiance. Additionally, controlled humidity annealed PSCs exhibit superior stability when aged under full spectrum simulated solar illumination at 85 °C and in open-circuit conditions.The promise of operational stability in pnictogen-based perovskite-inspired solar cells †
EES Solar Royal Society of Chemistry (2025)