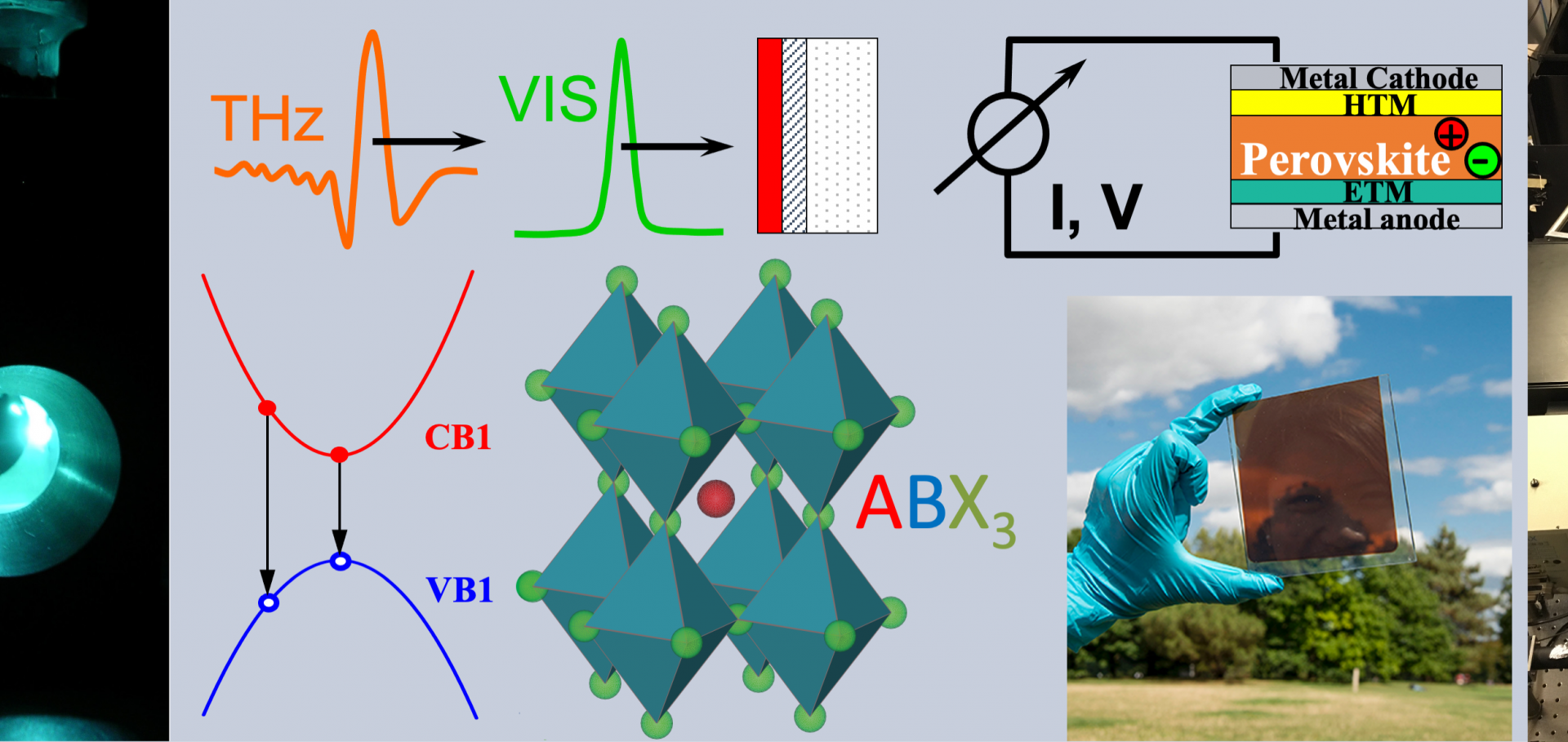
Photocurrent spectroscopy of perovskite solar cells over a wide temperature range from 15 to 350 K
Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters American Chemical Society 2018:9 (2017) 263-268
Abstract:
Solar cells based on metal halide perovskite thin films show great promise for energy generation in a range of environments from terrestrial installations to space applications. Here we assess the device characteristics of the prototypical perovskite solar cells based on methylammonium lead triiodide (CH3NH3PbI3) over a broad temperature range from 15 to 350 K (−258 to 77 °C). For these devices, we observe a peak in the short-circuit current density and open-circuit voltage at 200 K (−73 °C) with decent operation maintained up to 350 K. We identify the clear signature of crystalline PbI2 contributing directly to the low-temperature photocurrent spectra, showing that PbI2 plays an active role (beyond passivation) in CH3NH3PbI3 solar cells. Finally we observe a blue-shift in the photocurrent spectrum with respect to the absorption spectrum at low temperature (15 K), allowing us to extract a lower limit on the exciton binding energy of 9.1 meV for CH3NH3PbI3.Band Tail States in FAPbI3: Characterization and Simulation
Fundacio Scito (2017)
Fundamental mechanisms determining charge-carrier recombination and mobility in hybrid perovskites at the intrinsic limit
Fundacio Scito (2017)
Large-area, highly uniform evaporated formamidinium lead triiodide thin-films for solar cells
ACS Energy Letters American Chemical Society 2 (2017) 2799-2804
Abstract:
Perovskite thin-film solar cells are one of the most promising emerging renewable energy technologies because of their potential for low-cost, large-area fabrication combined with high energy conversion efficiencies. Recently, formamidinium lead triiodide (FAPbI3) and other formamidinium (CH(NH2)2) based perovskites have been explored as interesting alternatives to methylammonium lead triiodide (MAPbI3) because they exhibit better thermal stability. However, at present a major challenge is the scale-up of perovskite solar cells from small test-cells to full solar modules. We show that coevaporation is a scalable method for the deposition of homogeneous FAPbI3 thin films over large areas. The method allows precise control over film thickness and results in highly uniform, pinhole-free layers. Our films exhibited a high charge-carrier mobility of 26 cm2 V–1s–1, excellent optical properties, and a bimolecular recombination constant of 7 × 10–11 cm3 s–1. Solar cells fabricated using these vapor-deposited layers within a regular device architecture produced stabilized power conversion efficiencies of up to 14.2%. Thus, we demonstrate that efficient FAPbI3 solar cells can be vapor-deposited, which opens up a pathway toward large-area stable perovskite photovoltaics.Crystallization kinetics and morphology control of formamidinium-cesium mixed-cation lead mixed-halide perovskite via tunability of the colloidal precursor solution
Fundacio Scito (2017)