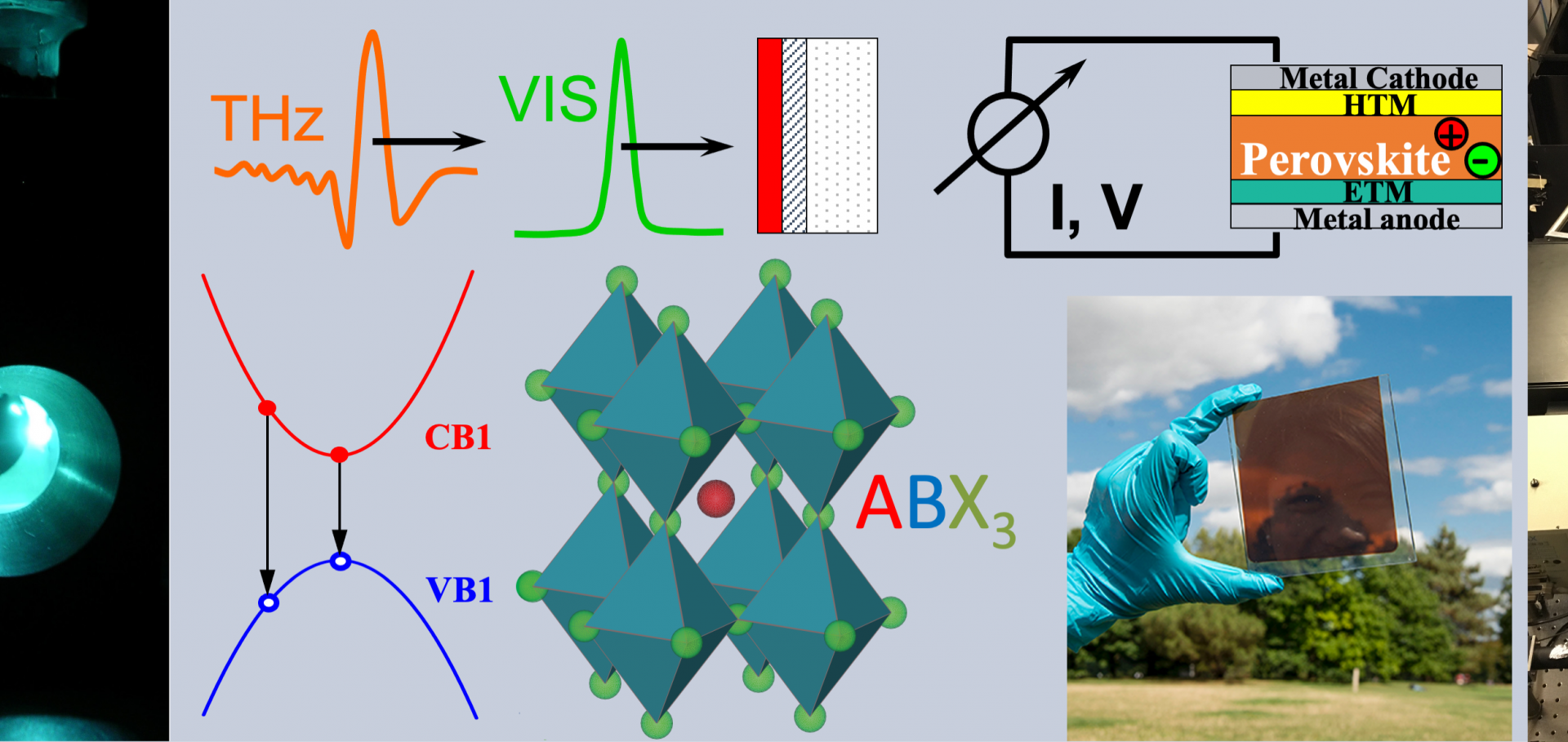
Degradation Mechanisms of Mixed Lead Tin and Tin Halide Perovskites
Fundacio Scito (2023)
Exciton formation dynamics and efficient free charge-carrier transport in 2D perovskite semiconductors
Fundacio Scito (2023)
Halide segregation in metal halide perovskites: effects on optoelectronic performance and reversibility
Fundacio Scito (2023)
Ultrafast Localisation and Charge Carrier Dynamics in Novel Bismuth Based Perovskite Inspired Materials
Fundacio Scito (2023)
Ultrafast self-localisation of charge carriers in next-generation bismuth halide and chalcogenide semiconductors
Fundacio Scito (2023)