Quantification of temperature-dependent charge separation and recombination dynamics in non-fullerene organic photovoltaics
Abstract:
Transient optical spectroscopy is used to quantify the temperature-dependence of charge separation and recombination dynamics in P3TEA:SF-PDI2 and PM6:Y6, two non-fullerene organic photovoltaic (OPV) systems with a negligible driving force and high photocurrent quantum yields. By tracking the intensity of the transient electroabsorption response that arises upon interfacial charge separation in P3TEA:SF-PDI2, a free charge generation rate constant of ≈2.4 × 1010 s−1 is observed at room temperature, with an average energy of ≈230 meV stored between the interfacial charge pairs. Thermally activated charge separation is also observed in PM6:Y6, and a faster charge separation rate of ≈5.5 × 1010 s−1 is estimated at room temperature, which is consistent with the higher device efficiency. When both blends are cooled down to cryogenic temperature, the reduced charge separation rate leads to increasing charge recombination either directly at the donor-acceptor interface or via the emissive singlet exciton state. A kinetic model is used to rationalize the results, showing that although photogenerated charges have to overcome a significant Coulomb potential to generate free carriers, OPV blends can achieve high photocurrent generation yields given that the thermal dissociation rate of charges outcompetes the recombination rate.Resonantly pumped bright-triplet exciton lasing in cesium lead bromide perovskites
Abstract:
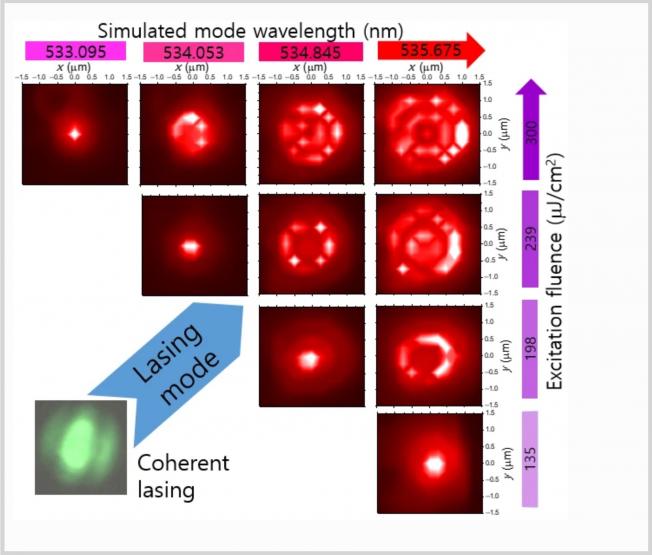
The surprising recent observation of highly emissive triplet-states in lead halide perovskites accounts for their orders-of-magnitude brighter optical signals and high quantum efficiencies compared to other semiconductors. This makes them attractive for future optoelectronic applications, especially in bright low-threshold nanolasers. While nonresonantly pumped lasing from all-inorganic lead-halide perovskites is now well-established as an attractive pathway to scalable low-power laser sources for nano-optoelectronics, here we showcase a resonant optical pumping scheme on a fast triplet-state in CsPbBr<sub>3</sub> nanocrystals. The scheme allows us to realize a polarized triplet-laser source that dramatically enhances the coherent signal by 1 order of magnitude while suppressing noncoherent contributions. The result is a source with highly attractive technological characteristics, including a bright and polarized signal and a high stimulated-to-spontaneous emission signal contrast that can be filtered to enhance spectral purity. The emission is generated by pumping selectively on a weakly confined excitonic state with a Bohr radius ∼10 nm in the nanocrystals. The exciton fine-structure is revealed by the energy-splitting resulting from confinement in nanocrystals with tetragonal symmetry. We use a linear polarizer to resolve 2-fold nondegenerate sublevels in the triplet exciton and use photoluminescence excitation spectroscopy to determine the energy of the state before pumping it resonantly.Exciton dynamics in monolayer graphene grown on a Cu(111) surface
Abstract:
We have characterized the carrier dynamics of the excitonic emission emerging from a monolayer of graphene grown on a Cu(111) surface. Excitonic emission from the graphene, with strong and sharp peaks both with a full-width at half-maximum of 2.7 meV, was observed near ~3.16 and ~3.18 eV at 4.2 K. The carrier recombination parameters were studied by measuring both temperature-dependent and time-resolved photoluminescence. The intensity variation with temperature of these two peaks shows an opposing trend. The time-resolved emission was modelled using coupled differential equations and the decay time was found to be dominated by carrier trapping and Auger recombination as the temperature increased.Resonantly pumped bright-triplet exciton lasing in caesium lead bromide perovskites
Imaging nonradiative point defects buried in quantum wells using cathodoluminescence
Abstract:
Crystallographic point defects (PDs) can dramatically decrease the efficiency of optoelectronic semiconductor devices, many of which are based on quantum well (QW) heterostructures. However, spatially resolving individual nonradiative PDs buried in such QWs has so far not been demonstrated. Here, using high-resolution cathodoluminescence (CL) and a specific sample design, we spatially resolve, image, and analyze nonradiative PDs in InGaN/GaN QWs at the nanoscale. We identify two different types of PDs by their contrasting behavior with temperature and measure their densities from 1014 cm–3 to as high as 1016 cm–3. Our CL images clearly illustrate the interplay between PDs and carrier dynamics in the well: increasing PD concentration severely limits carrier diffusion lengths, while a higher carrier density suppresses the nonradiative behavior of PDs. The results in this study are readily interpreted directly from CL images and represent a significant advancement in nanoscale PD analysis.