Thickness-dependent topological phases and flat bands in rhombohedral multilayer graphene
Science Bulletin Elsevier (2025)
Layer-dependent exciton dynamics in InSe/WS2 heterostructures
CHINESE PHYSICS B 34:9 (2025) ARTN 097802
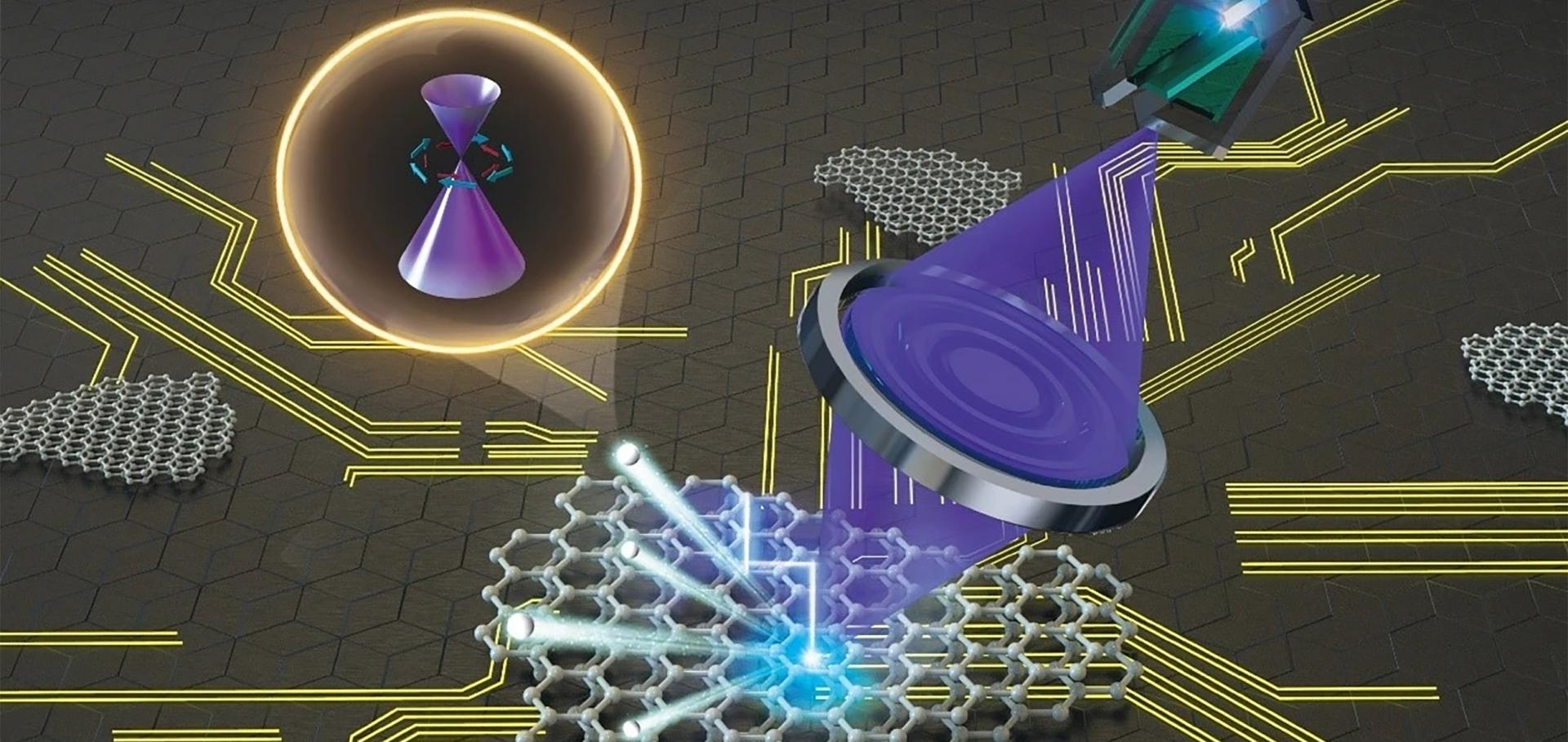
Topological phase transition in quasi-one-dimensional bismuth iodide Bi 4 I 4
npj Quantum Materials Nature Research 9:1 (2024) 103
Abstract:
Quasi-one-dimensional (quasi-1D) bismuth iodide Bi4I4 exhibits versatile topological phases of matter including weak topological insulator (WTI) and higher-order topological insulator (HOTI) phases with high tunability in response to external parameters. In this work, performing laser-based angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy with submicron spatial resolution (micro-ARPES), we reveal the presence of an energy gap on the (100) surface of the low-temperature α-Bi4I4, providing spectroscopic evidence for the HOTI phase. Conversely, the high-temperature β-Bi4I4 harbors gapless Dirac fermions on the (100) surface alongside gapped states on the (001) surface, thereby establishing a WTI phase. By tracking the temperature evolution of the (100) surface states, we unveil a thermal hysteresis of the surface gap in line with the α-β structural phase transition. Our findings directly evidence a temperature-induced topological phase transition from WTI to HOTI in Bi4I4, which paves the way to its potential applications at room temperature.Strong electron–phonon coupling in magic-angle twisted bilayer graphene
Nature Nature Research 636:8042 (2024) 342-347
Abstract:
The unusual properties of superconductivity in magic-angle twisted bilayer graphene (MATBG) have sparked considerable research interest1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12–13. However, despite the dedication of intensive experimental efforts and the proposal of several possible pairing mechanisms14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23–24, the origin of its superconductivity remains elusive. Here, by utilizing angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy with micrometre spatial resolution, we reveal flat-band replicas in superconducting MATBG, where MATBG is unaligned with its hexagonal boron nitride substrate11. These replicas show uniform energy spacing, approximately 150 ± 15 meV apart, indicative of strong electron–boson coupling. Strikingly, these replicas are absent in non-superconducting twisted bilayer graphene (TBG) systems, either when MATBG is aligned to hexagonal boron nitride or when TBG deviates from the magic angle. Calculations suggest that the formation of these flat-band replicas in superconducting MATBG are attributed to the strong coupling between flat-band electrons and an optical phonon mode at the graphene K point, facilitated by intervalley scattering. These findings, although they do not necessarily put electron–phonon coupling as the main driving force for the superconductivity in MATBG, unravel the electronic structure inherent in superconducting MATBG, thereby providing crucial information for understanding the unusual electronic landscape from which its superconductivity is derived.Disassembling one-dimensional chains in molybdenum oxides
Chinese Physics B IOP Publishing 33:12 (2024) 127102