Ultrafast spontaneous exciton dissociation via phonon emission in BiVO4
Physical Review Research American Physical Society (APS) 8:1 (2026) 013105
Abstract:
Monoclinic bismuth vanadate ( ) is a promising indirect band gap semiconductor for photoelectrochemical water splitting, yet the characteristics of its low-lying photoexcitations, or excitons, remain poorly understood. Here, we use an Bethe-Salpeter equation approach that incorporates phonon screening to compute the nature and lifetimes of the low-lying excitons of . Our calculations indicate that at 0 K, the lowest-lying exciton energy exceeds the indirect band gap, enabling spontaneous dissociation into free carriers via phonon emission within picoseconds. At 300 K, both phonon emission and absorption effects reduce this timescale to only a few femtoseconds. Phonon screening also greatly reduces the binding energy of the lowest-lying exciton, leading to an optical absorption spectrum that better reproduces experimental measurements. Overall, our findings establish the general conditions under which phonon emission-driven exciton dissociation can occur in indirect gap semiconductors, and they emphasize the critical role phonon screening can play in predictive calculations of photophysical properties of complex materials.Twisted Tin‐Chloride Perovskite Single‐Crystal Heterostructures
Angewandte Chemie International Edition Wiley (2025) e20140
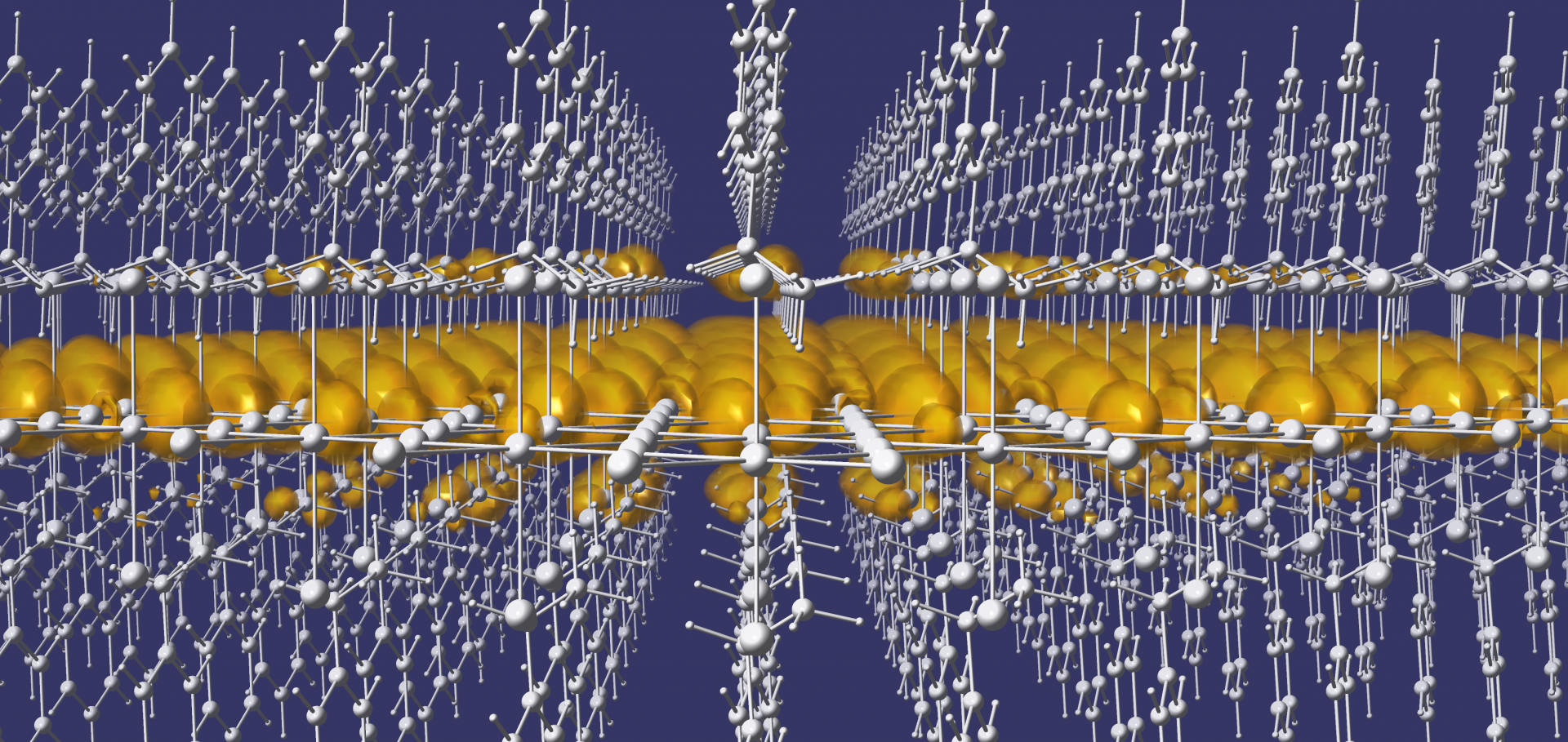
Abstract:
Self‐assembly affords simpler synthetic routes to heterostructures compared with manual layer‐by‐layer stacking, yet controlling interlayer twist angles in a bulk solid remains an outstanding challenge. We report two new single‐crystal heterostructures: (Sn2Cl2)(CYS)2SnCl4 (CYS = +NH3(CH2)2S–; Sn_CYS) and (Sn2Cl2)(SeCYS)2SnCl4 (SeCYS = +NH3(CH2)2Se–; Sn_SeCYS) synthesized in solution, with alternating perovskite and intergrowth layers. Notably, compared to the recently reported lead analog, (Pb2Cl2)(CYS)2PbCl4 (Pb_CYS), the tin heterostructures feature a twist between the perovskite and intergrowth layers. We trace this twist to local distortions at the Sn centers, which change the interfacial lattice‐matching requirements compared to those of the Pb analog. Electronic band structure calculations show that the striking differences in the relative energies of perovskite‐ and intergrowth‐derived bands in Sn_CYS and Pb_CYS arise from structural and not compositional differences. The structural anisotropy of Sn_CYS is also reflected in a large in‐plane photoluminescence linear anisotropy ratio. Interfacial strain further affords differential incorporation of Pb into the perovskite and intergrowth layers of the Sn heterostructures, resulting in redshifted optical absorption onsets. Thus, we posit that local structural distortions may be exploited to manipulate the twist angle and interfacial strain in bulk heterostructures, providing a new handle for tuning the band alignments of bulk quantum‐well electronic structures.Addition to “Tuning the Quantum-Well Structure of Single-Crystal Layered Perovskite Heterostructures”
Journal of the American Chemical Society American Chemical Society (ACS) 147:49 (2025) 45840-45840
Twisted Tin‐Chloride Perovskite Single‐Crystal Heterostructures
Angewandte Chemie (2025)
Abstract:
Self‐assembly affords simpler synthetic routes to heterostructures compared with manual layer‐by‐layer stacking, yet controlling interlayer twist angles in a bulk solid remains an outstanding challenge. We report two new single‐crystal heterostructures: (Sn2Cl2)(CYS)2SnCl4 (CYS = +NH3(CH2)2S–; Sn_CYS) and (Sn2Cl2)(SeCYS)2SnCl4 (SeCYS = +NH3(CH2)2Se–; Sn_SeCYS) synthesized in solution, with alternating perovskite and intergrowth layers. Notably, compared to the recently reported lead analog, (Pb2Cl2)(CYS)2PbCl4 (Pb_CYS), the tin heterostructures feature a twist between the perovskite and intergrowth layers. We trace this twist to local distortions at the Sn centers, which change the interfacial lattice‐matching requirements compared to those of the Pb analog. Electronic band structure calculations show that the striking differences in the relative energies of perovskite‐ and intergrowth‐derived bands in Sn_CYS and Pb_CYS arise from structural and not compositional differences. The structural anisotropy of Sn_CYS is also reflected in a large in‐plane photoluminescence linear anisotropy ratio. Interfacial strain further affords differential incorporation of Pb into the perovskite and intergrowth layers of the Sn heterostructures, resulting in redshifted optical absorption onsets. Thus, we posit that local structural distortions may be exploited to manipulate the twist angle and interfacial strain in bulk heterostructures, providing a new handle for tuning the band alignments of bulk quantum‐well electronic structures. Replacing lead with tin in a single‐crystal halide perovskite heterostructure drives a twist between the perovskite (gray) and intergrowth (blue) layers. The accompanying structural distortions and interfacial strain change the calculated orbital composition of the band edges and enable high in‐plane optical anisotropy in the Sn analog. (VBT = valence band top; CBB = conduction band bottom).Tailoring a Lead-Free Organic–Inorganic Halobismuthate for Large Piezoelectric Effect
Journal of the American Chemical Society American Chemical Society 147:49 (2025) 45366-45376