Correction to “A Templating Approach to Controlling the Growth of Coevaporated Halide Perovskites”
Roadmap on Photovoltaic Absorber Materials for Sustainable Energy Conversion
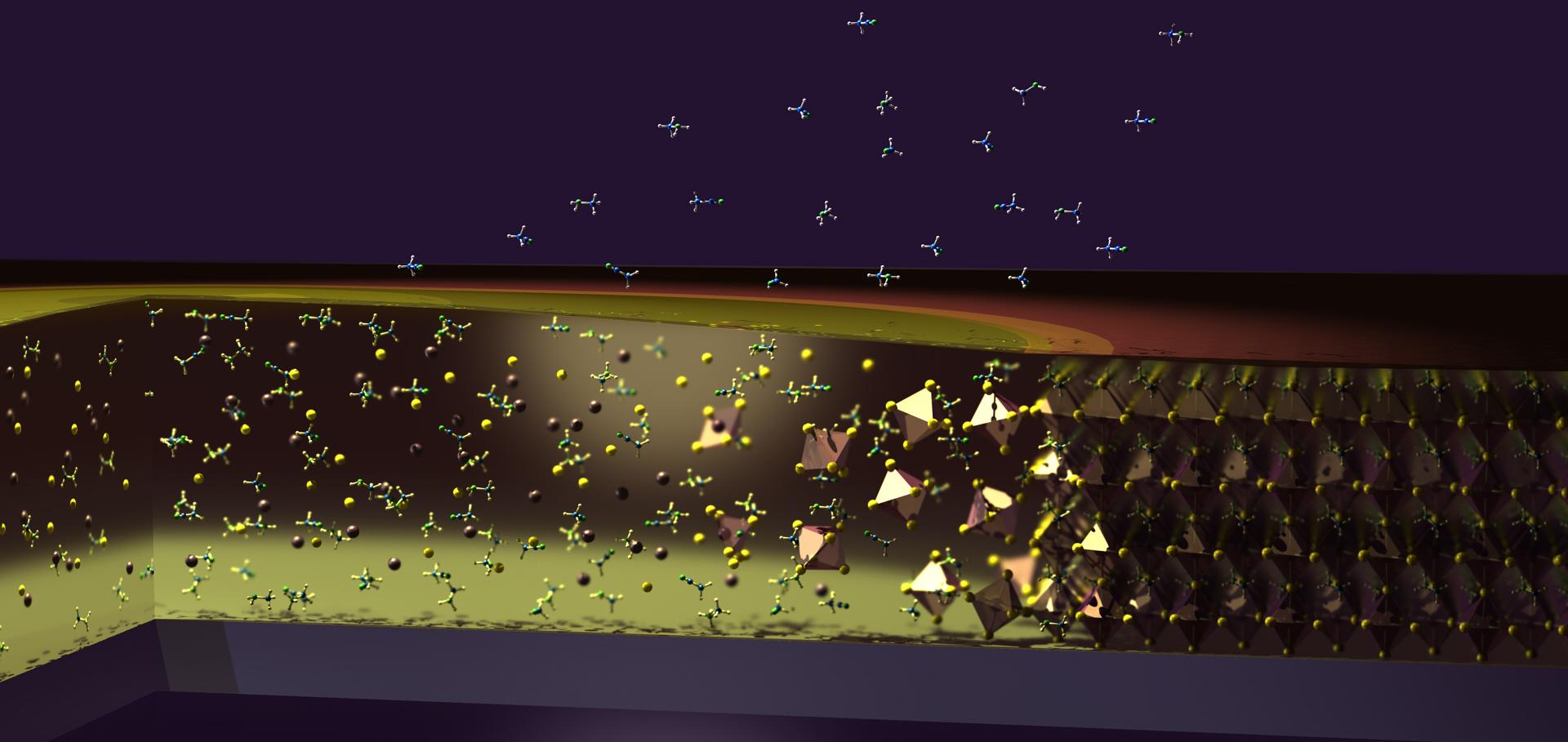
A templating approach to controlling the growth of coevaporated halide perovskites
Abstract:
Metal halide perovskite semiconductors have shown significant potential for use in photovoltaic (PV) devices. While fabrication of perovskite thin films can be achieved through a variety of techniques, thermal vapor deposition is particularly promising, allowing for high-throughput fabrication. However, the ability to control the nucleation and growth of these materials, particularly at the charge-transport layer/perovskite interface, is critical to unlocking the full potential of vapor-deposited perovskite PV. In this study, we explore the use of a templating layer to control the growth of coevaporated perovskite films and find that such templating leads to highly oriented films with identical morphology, crystal structure, and optoelectronic properties independent of the underlying layers. Solar cells incorporating templated FA0.9Cs0.1PbI3–xClx show marked improvements with steady-state power conversion efficiency over 19.8%. Our findings provide a straightforward and reproducible method of controlling the charge-transport layer/coevaporated perovskite interface, further clearing the path toward large-scale fabrication of efficient PV devices.Contrasting charge-carrier dynamics across key metal-halide perovskite compositions through in situ simultaneous probes
Abstract:
Metal-halide perovskites have proven to be a versatile group of semiconductors for optoelectronic applications, with ease of bandgap tuning and stability improvements enabled by halide and cation mixing. However, such compositional variations can be accompanied by significant changes in their charge-carrier transport and recombination regimes that are still not fully understood. Here, a novel combinatorial technique is presented to disentangle such dynamic processes over a wide range of temperatures, based on transient free-space, high-frequency microwave conductivity and photoluminescence measurements conducted simultaneously in situ. Such measurements are used to reveal and contrast the dominant charge-carrier recombination pathways for a range of key compositions: prototypical methylammonium lead iodide perovskite (MAPbI3), the stable mixed formamidinium-caesium lead-halide perovskite FA0.83Cs0.17PbBr0.6I2.4 targeted for photovoltaic tandems with silicon, and fully inorganic wide-bandgap CsPbBr3 aimed toward light sources and X-ray detector applications. The changes in charge-carrier dynamics in FA0.83Cs0.17PbBr0.6I2.4 across temperatures are shown to be dominated by radiative processes, while those in MAPbI3 are governed by energetic disorder at low temperatures, low-bandgap minority-phase inclusions around the phase transition, and non-radiative processes at room temperature. In contrast, CsPbBr3 exhibits significant charge-carrier trapping at low and high temperatures, highlighting the need for improvement of material processing techniques for wide-bandgap perovskites.Photovoltaic performance of FAPbI3 perovskite is hampered by intrinsic quantum confinement
Abstract:
Formamidinium lead trioiodide (FAPbI3) is a promising perovskite for single-junction solar cells. However, FAPbI3 is metastable at room temperature and can cause intrinsic quantum confinement effects apparent through a series of above-bandgap absorption peaks. Here, we explore three common solution-based film-fabrication methods, neat N,N-dimethylformamide (DMF)–dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) solvent, DMF-DMSO with methylammonium chloride, and a sequential deposition approach. The latter two offer enhanced nucleation and crystallization control and suppress such quantum confinement effects. We show that elimination of these absorption features yields increased power conversion efficiencies (PCEs) and short-circuit currents, suggesting that quantum confinement hinders charge extraction. A meta-analysis of literature reports, covering 244 articles and 825 photovoltaic devices incorporating FAPbI3 films corroborates our findings, indicating that PCEs rarely exceed a 20% threshold when such absorption features are present. Accordingly, ensuring the absence of these absorption features should be the first assessment when designing fabrication approaches for high-efficiency FAPbI3 solar cells.