Carbon Nanotubes - the p-Type Contact of the Future for Perovskite Solar Cells?
ECS Meeting Abstracts The Electrochemical Society MA2018-01:5 (2018) 643-643
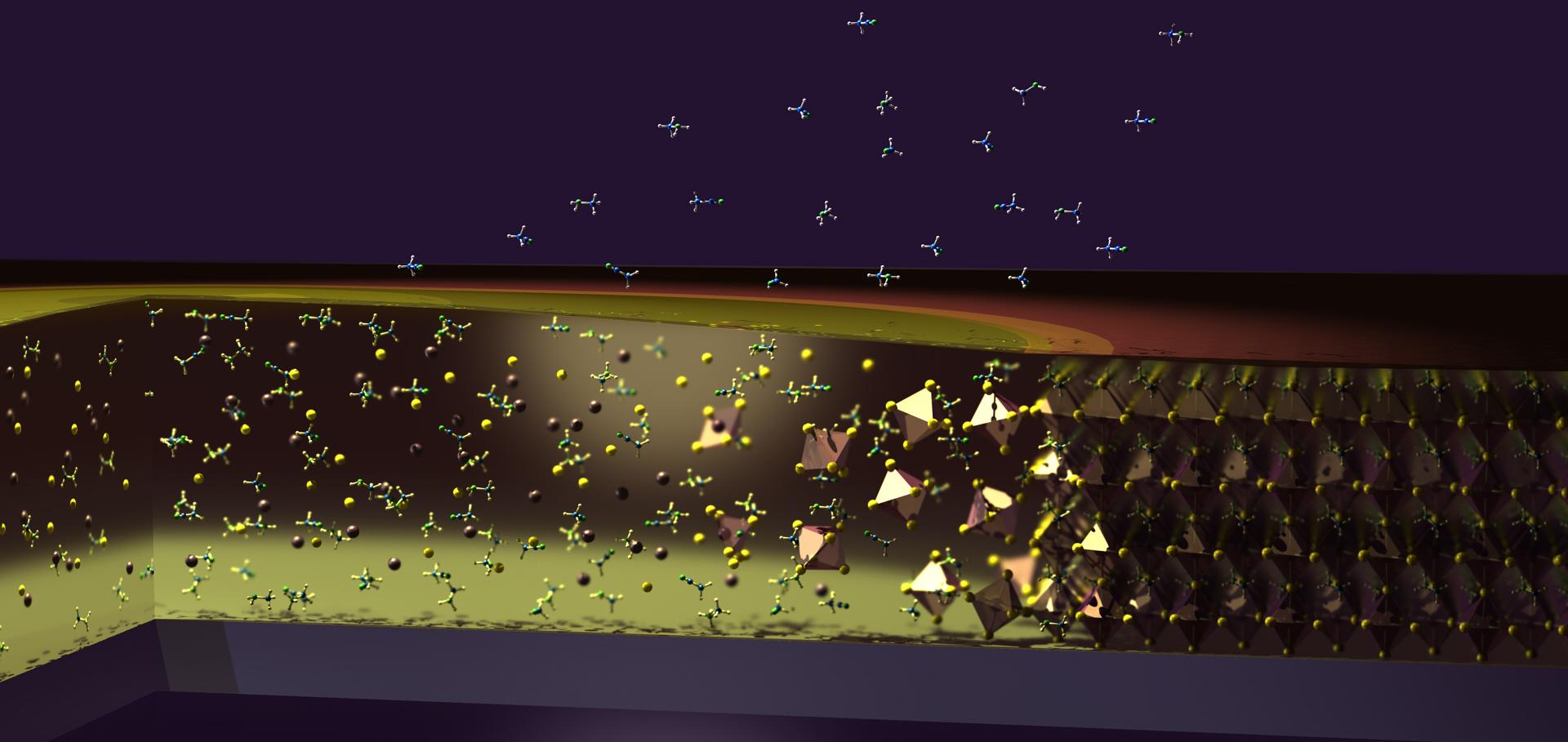
Crystallization kinetics and morphology control of formamidinium-cesium mixed-cation lead mixed-halide perovskite via tunability of the colloidal precursor solution
Fundacio Scito (2017)
Unveiling the influence of pH on the crystallization of hybrid perovskites, felivering low voltage loss photovoltaics
Joule Cell Press 1:2 (2017) 328-343
Abstract:
Impressive power conversion efficiencies coupled with the relative ease of fabrication have made perovskite solar cells a front runner for next-generation photovoltaics. Although perovskite films and optoelectronic devices have been widely studied, relatively little is known about the chemistry of the precursor solutions. Here, we present a study on the hydrolysis of N,N-dimethylformamide, correlating how pH changes related to its degradation affect the crystallization of MAPbI3xClx perovskite films. By careful manipulation of the pH, and the resulting colloid distribution in precursor solutions, we fabricate perovskite films with greatly improved crystallinity, which when incorporated into photovoltaic devices reproducibly yield efficiencies of over 18%. Extending this method to the mixed cation, mixed halide perovskite FA0.83MA0.17Pb(I0.83Br0.17)3, we obtain power conversion efficiencies of up to 19.9% and open-circuit voltages of 1.21 V for a material with a bandgap of 1.57 eV, achieving the lowest yet reported loss in potential from bandgap to a VOC of only 360 mV.Consolidation of the optoelectronic properties of CH3NH3PbBr3 perovskite single crystals.
Nature Communications Springer Nature 8 (2017) 590
Abstract:
Ultralow trap densities, exceptional optical and electronic properties have been reported for lead halide perovskites single crystals; however, ambiguities in basic properties, such as the band gap, and the electronic defect densities in the bulk and at the surface prevail. Here, we synthesize single crystals of methylammonium lead bromide (CH3NH3PbBr3), characterise the optical absorption and photoluminescence and show that the optical properties of single crystals are almost identical to those of polycrystalline thin films. We observe significantly longer lifetimes and show that carrier diffusion plays a substantial role in the photoluminescence decay. Contrary to many reports, we determine that the trap density in CH3NH3PbBr3 perovskite single crystals is 1015 cm-3, only one order of magnitude lower than in the thin films. Our enhanced understanding of optical properties and recombination processes elucidates ambiguities in earlier reports, and highlights the discrepancies in the estimation of trap densities from electronic and optical methods.Metal halide perovskites for optoelectronic devices have been extensively studied in two forms: single-crystals or polycrystalline thin films. Using spectroscopic approaches, Wenger et al. show that polycrystalline thin films possess similar optoelectronic properties to single crystals.Metal Halide Perovskite Polycrystalline Films Exhibiting Properties of Single Crystals
Joule Elsevier 1:1 (2017) 155-167